Diabetes is a group of metabolic diseases characterized by hyperglycemia resulting from defects in insulin secretion, insulin action, or both. The chronic hyperglycemia of diabetes is associated with long-term damage, dysfunction, and failure of various organs, especially the eyes, kidneys, nerves, heart, and blood vessels.
HFHSD+STZ induced type II diabetes model in SD rat
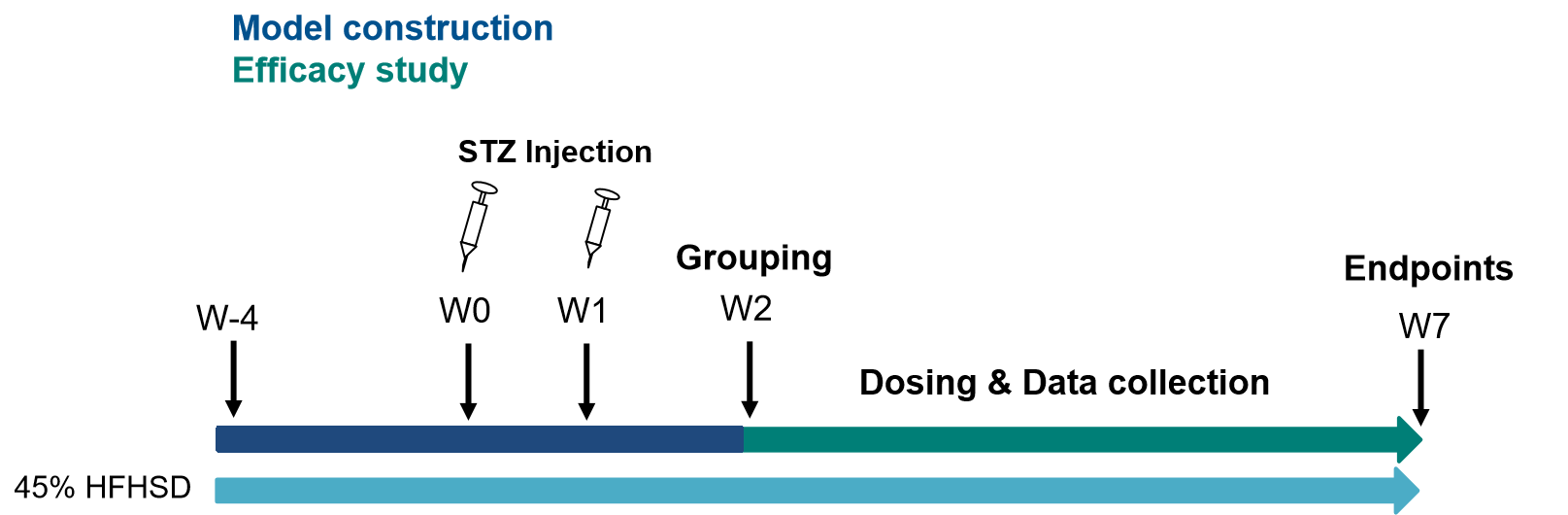
Figure1. Overview of pharmacodynamic evaluation on type II diabetes rat model
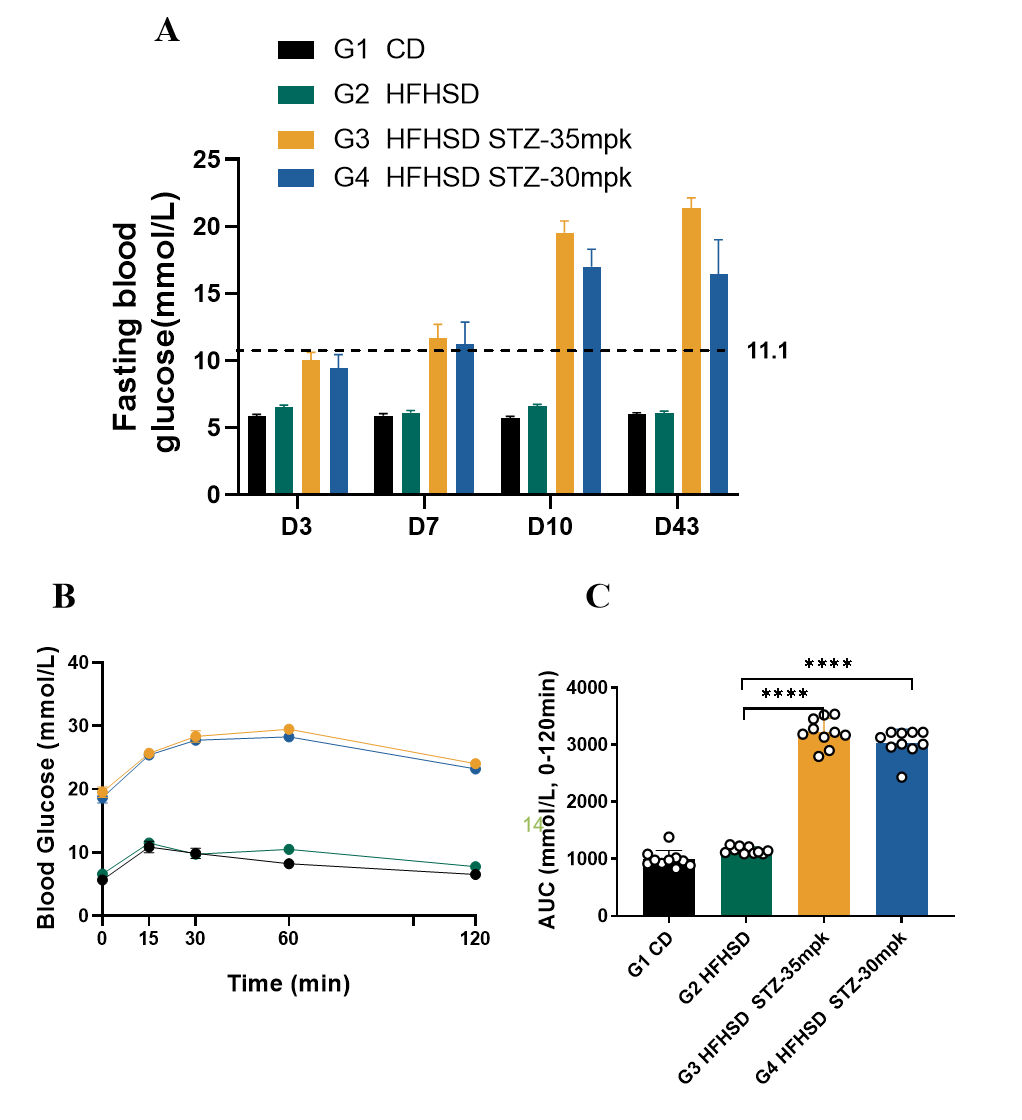
Figure2. HFHSD+STZ induced type II diabetes model in SD rat
HFHSD+STZ induced type II diabetic rats model demonstrated prolonged hyperglycemic states with postprandial blood glucose levels significantly elevated(Fig. 1A). Impaired glucose tolerance was observed in HFHSD+STZ induced type II diabetic rats model via OGTT test(Fig. 2B-C). Data were presented by mean ± SEM, N=8-10. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001 and ****, p < 0.0001
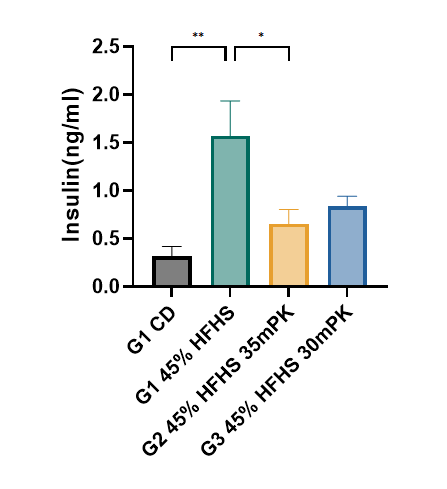
Figure3. Insulin content of HFHSD+STZ induced type II diabetes model in SD rat
HFHSD+STZ induced type II diabetic rats model demonstrated higher insulin levels than control group. Data were presented by mean ± SEM, N=8-10. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001 and ****, p < 0.0001

