Liver fibrosis is a pathological wound-healing response to chronic liver injury characterized by excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins that disrupt normal liver structure. Common causes include viral hepatitis, alcohol abuse, metabolic dysfunction, and toxic impairment. If left untreated, fibrosis may progress to cirrhosis, portal hypertension, and liver failure.
CCL4-induced chronic liver fibrosis models in SD rat
CCl4 generates toxic free radicals via CYP2E1 metabolism, causing lipid peroxidation, necrosis, and activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs). The CCl4-induced liver fibrosis model is a gold-standard preclinical system for studying hepatic fibrogenesis, mimicking human progression from hepatocyte injury → inflammation → fibrosis → cirrhosis.
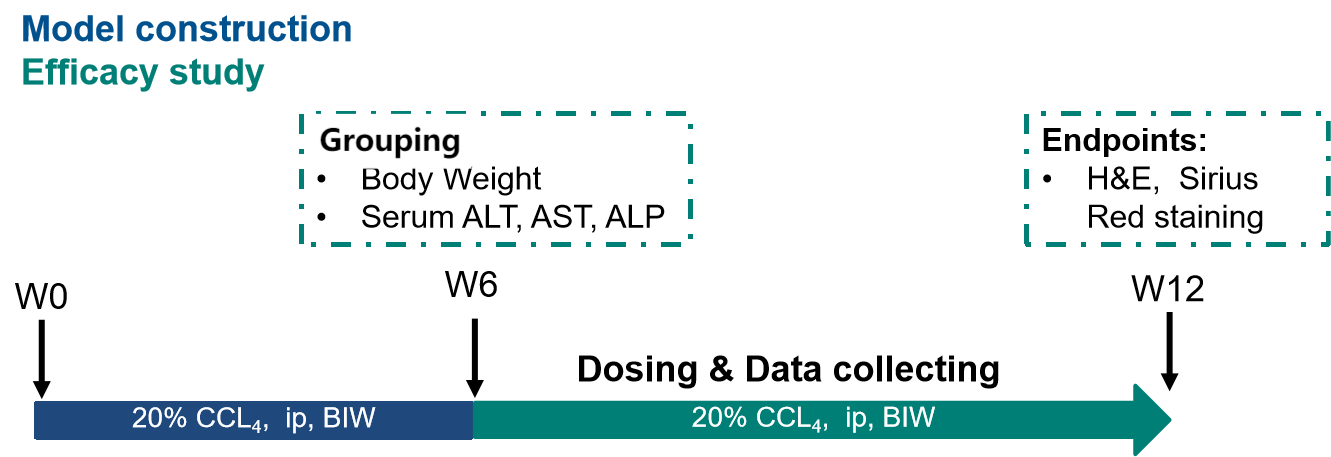
Fig.1 Overview of pharmacodynamic evaluation on CCL4-induced rat chronic liver fibrosis models
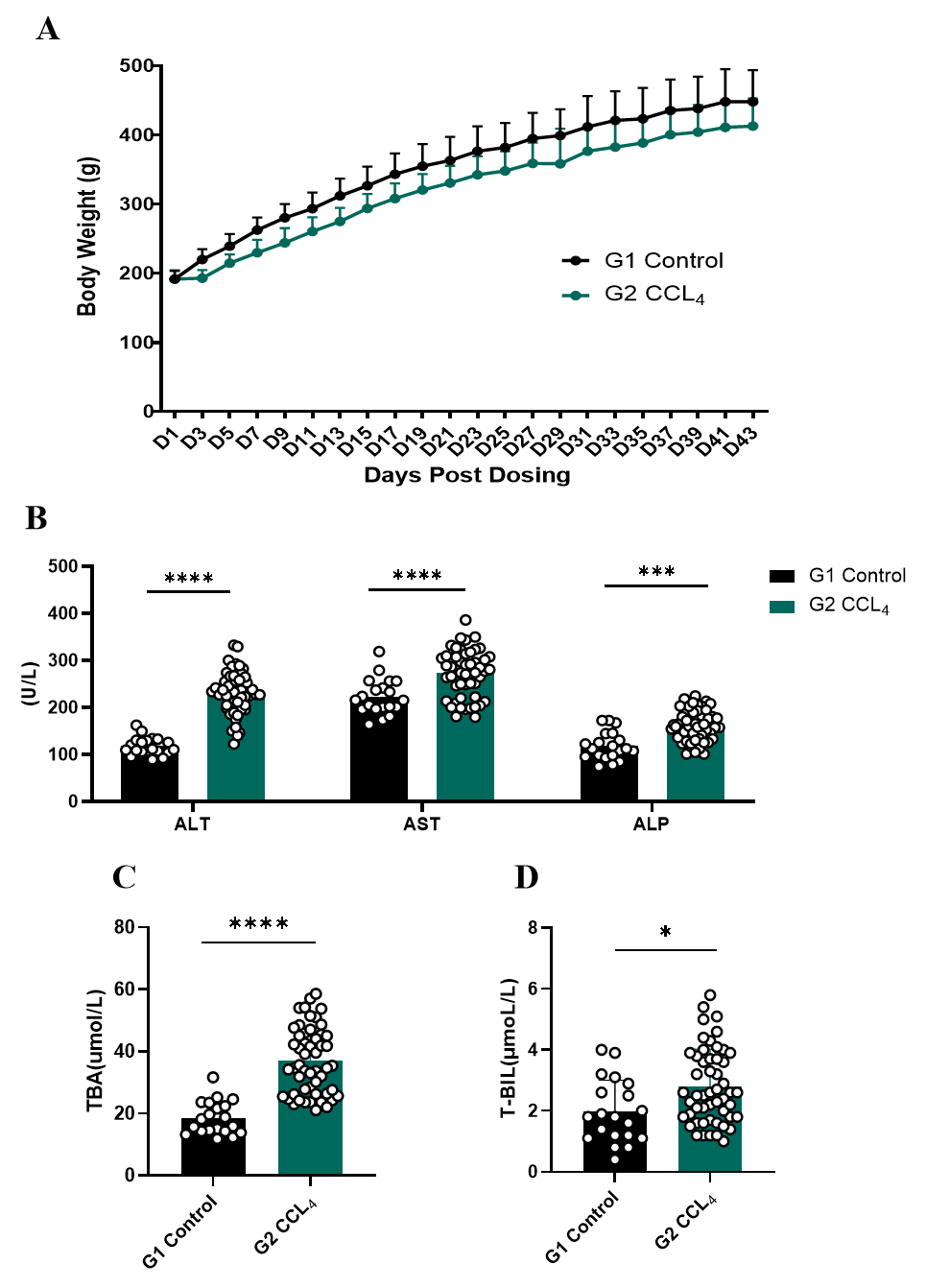
Fig.2 Body weight and serum ALT, AST, ALP, TBA and T-BIL of CCL4-induced rat chronic liver fibrosis models
Body weight curve of CCL4-induced rat chronic liver fibrosis models is shown in Fig. 2A. The serum level of ALT, AST, ALP, TBA and T-BIL were significantly higher in CCL4-induced rat chronic liver fibrosis models compared to the control group (Fig. 2B-D). Data were presented by mean ± SEM, N=25-45. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001 and ****, p < 0.0001
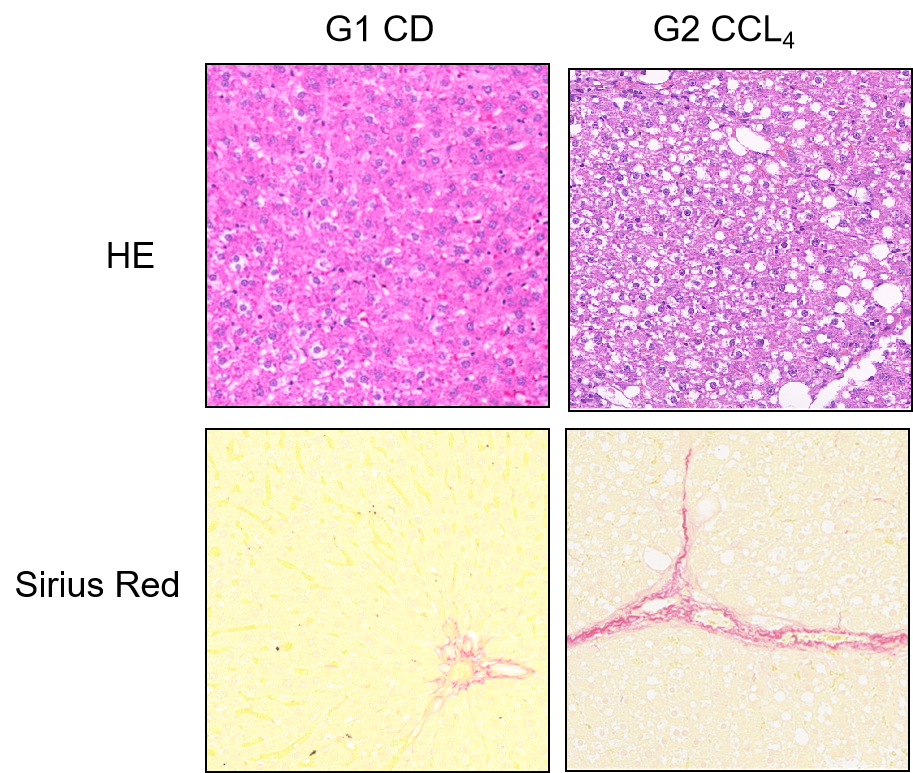
Fig.3 Histological observation of CCL4-induced rat chronic liver fibrosis models
Histopathological staining (HE and Sirius Red) showed significant vacuolar degeneration and fibrous tissue hyperplasia in CCL4-induced rat chronic liver fibrosis models.

