Pulmonary function testing in mice provides essential data for understanding respiratory physiology and pathophysiology in preclinical research. These tests enable researchers to quantify lung mechanics, evaluate disease progression, and assess therapeutic interventions in mouse models of various respiratory conditions.
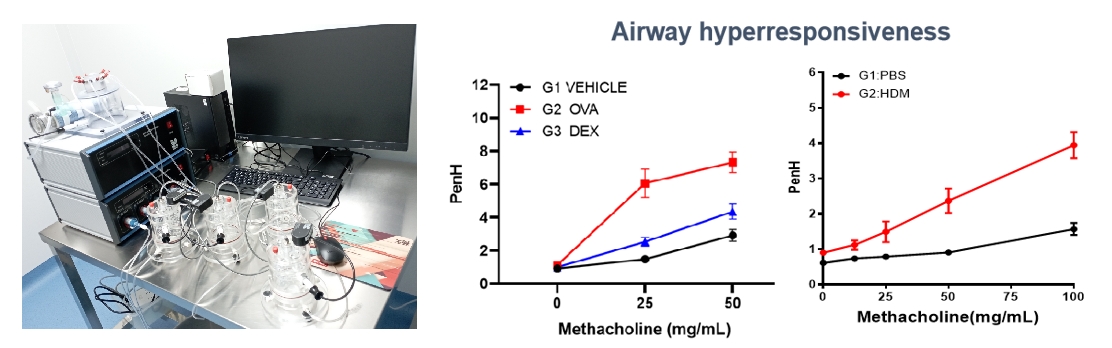
● Whole Body Plethysmography——Non-Invasive
Whole body plethysmography (WBP) is a non-invasive technique for assessing respiratory function in conscious mice, providing valuable data on breathing patterns without requiring anesthesia or animal restraint. These tests are commonly used in asthma models to evaluate airway hyperresponsiveness through challenge tests such as methacholine exposure.
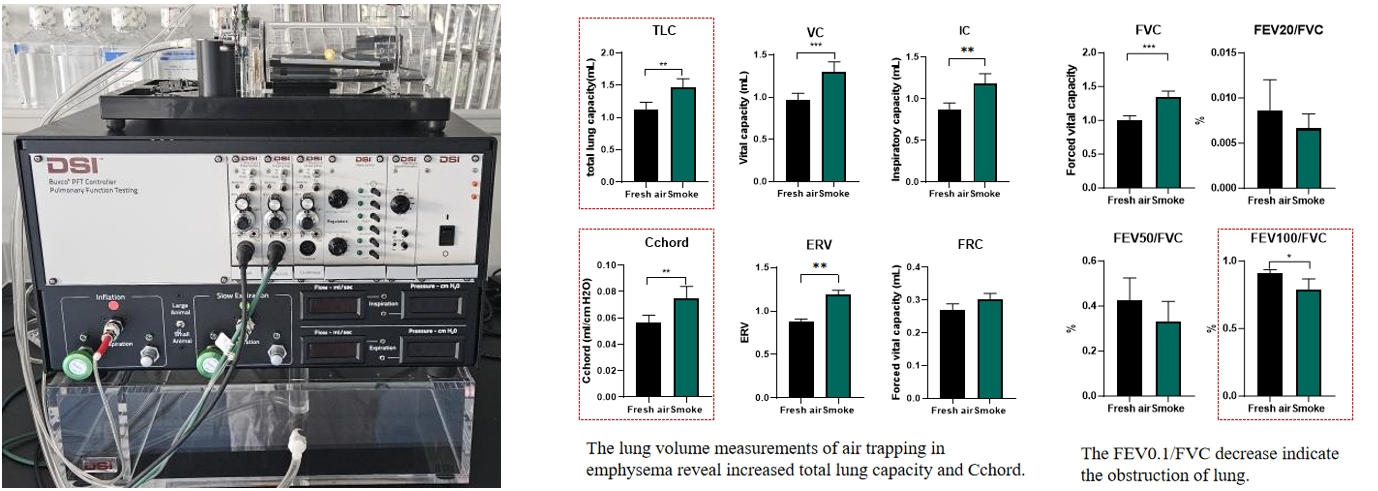
● Pulmonary function test——Invasive
Similar to human spirometry, these measurements assess lung volumes such as total lung capacity, functional residual capacity, vital capacity, and forced expiratory volumes. Invasive machines are commonly used for respiratory function evaluation in models such as COPD or IPF.