Acute lung injury is a serious respiratory condition characterized by acute pulmonary inflammation with disruption of the pulmonary vasculature endothelial and alveolar epithelial barriers. It can occur from various causes including pulmonary infections, trauma, sepsis, and certain drugs, resulting in hypoxemia and diffuse pulmonary infiltrates visible on chest imaging, and often referred to by its most severe subset known as acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).
Validation data
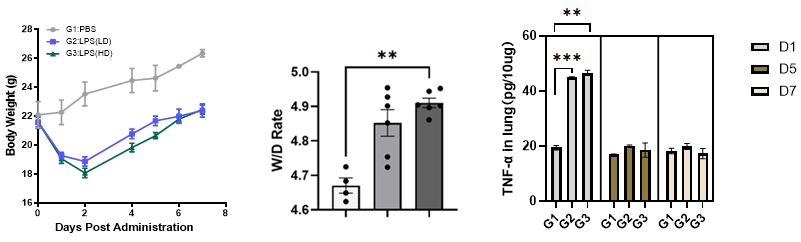
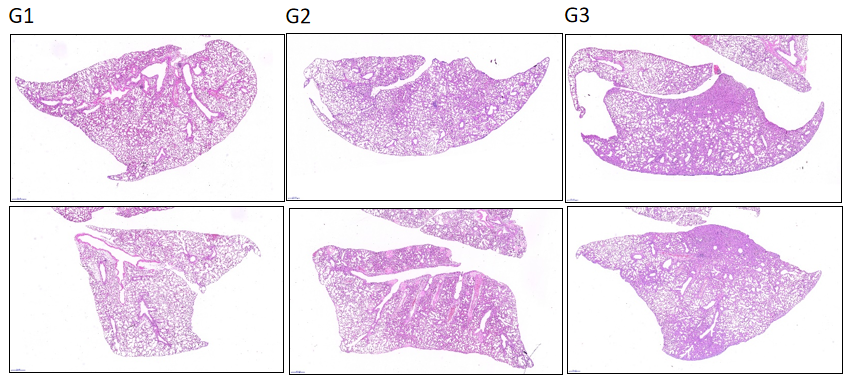
Both low and high doses of LPS can effectively induce acute lung injury and inflammatory cytokine secretion as evidenced in H&E stained sections.
Drug efficacy evaluation
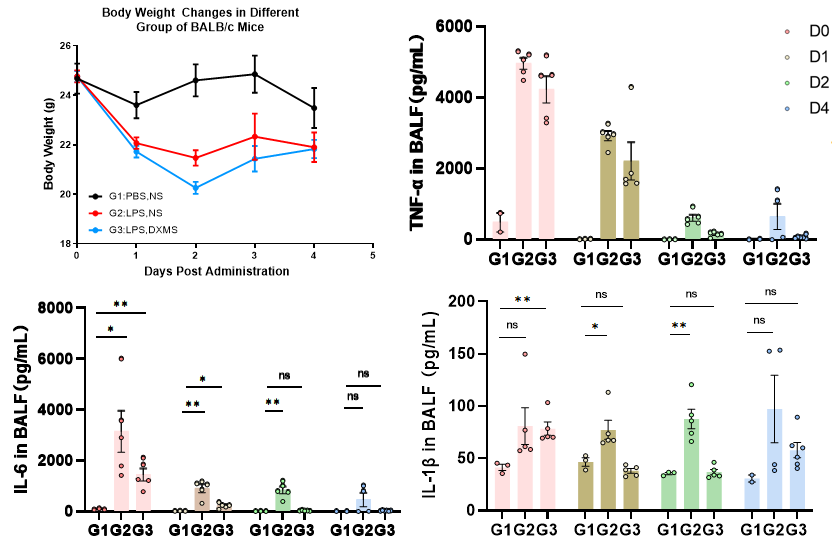
Dexamethasone can effectively reduce the secretion of inflammatory factors caused by acute lung injury.
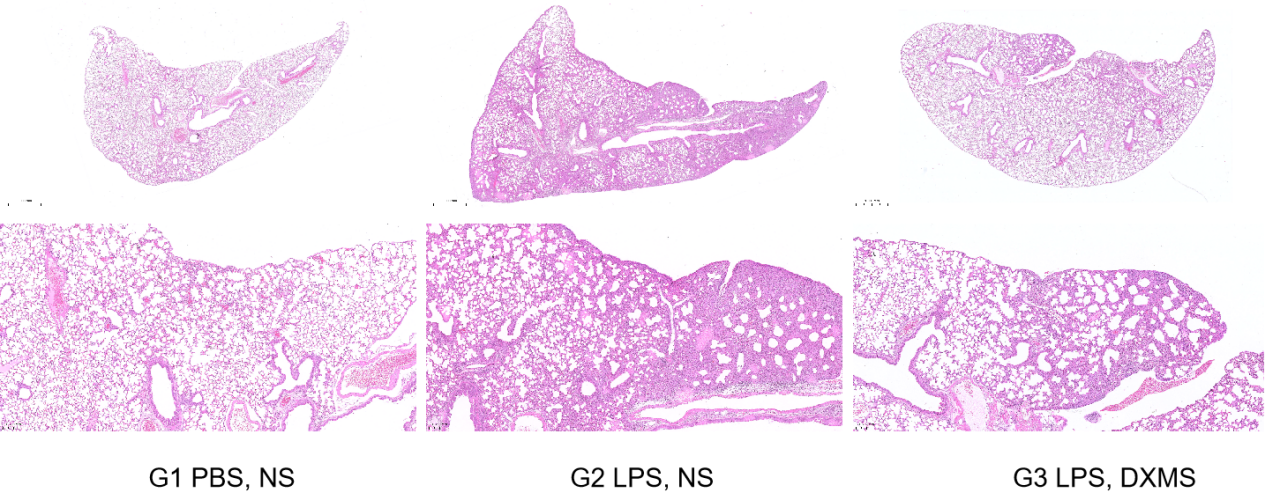
H&E staining results of pathological sections showed that dexamethasone could effectively relieve lung inflammation (D4).

