The dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced IBD mouse model uses DSS (MW 36,000 - 50,000), a sulfated polysaccharide. Administering DSS to mice damages colonic epithelial cells, impairing mucosal barriers and leading to ulcerative colitis (UC) - like conditions. These mice show symptoms similar to those observed in human IBD patients, including weight loss, diarrhea, and fecal occult blood. Acute DSS colitis involves neutrophil and macrophage activation, with Th1, Th17, and Treg cells also participating. This model is useful for studying IBD pathogenesis and treatments.
DSS Induced Acute IBD Model
Acute UC model which resembles the histological changes in UC patients
Widely used and easy to establish
Short experiment period and relatively low cost
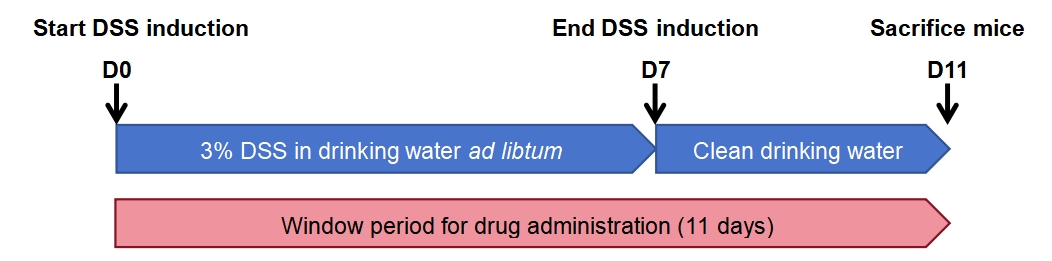
Modeling strategy: C57BL/6JGpt, male; DSS induced
Validation data: DSS-induced IBD model for efficacy evaluation of cyclosporine A
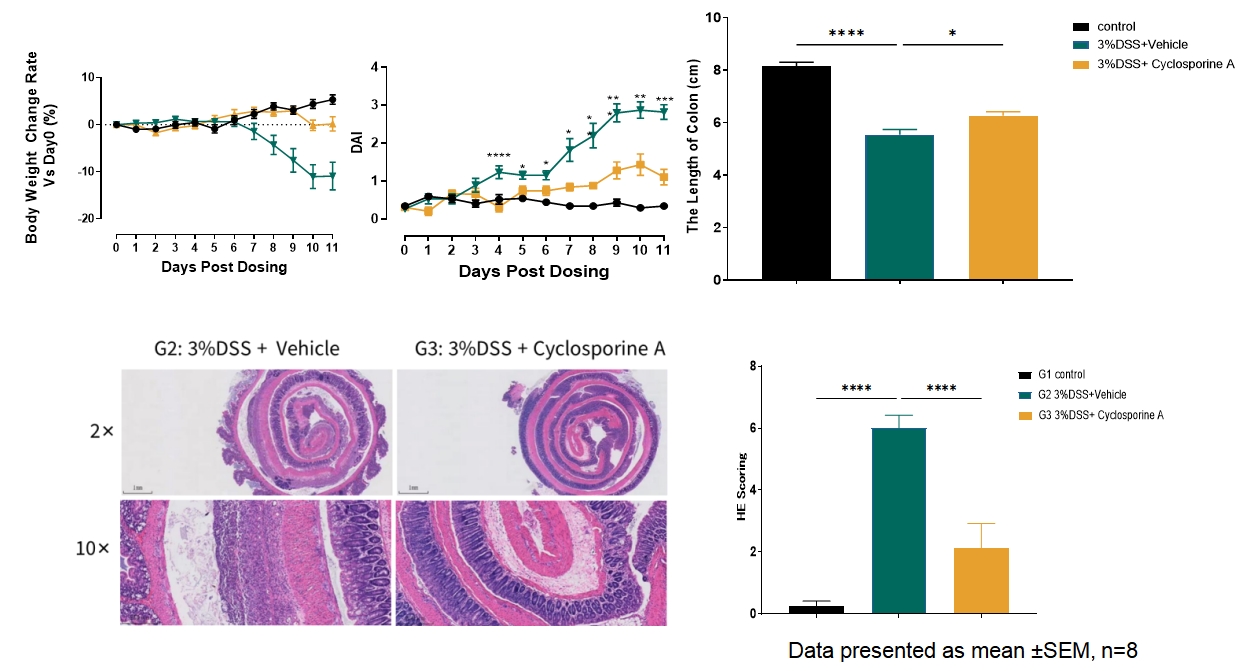
The treatment with cyclosporine A ameliorated the DAI score, increased the colon length and decreased the HE score in IBD models induced by DSS.
DSS-induced chronic colitis model
Experimental mouse strains: B6, 6-7weeks old, male
Modeling cell: 3% DSS
Modeling method:
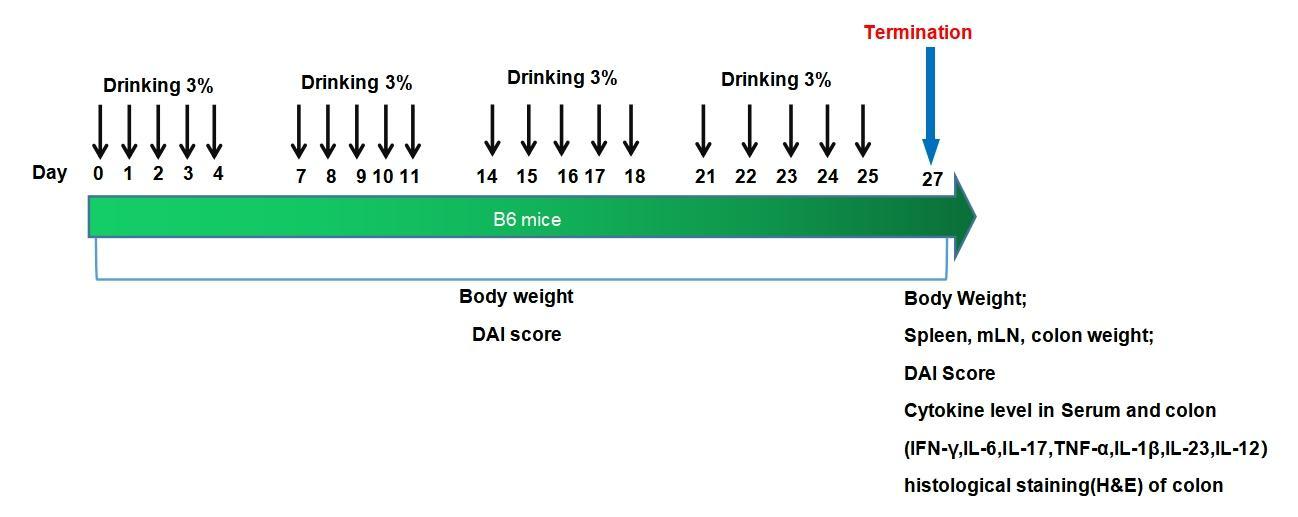
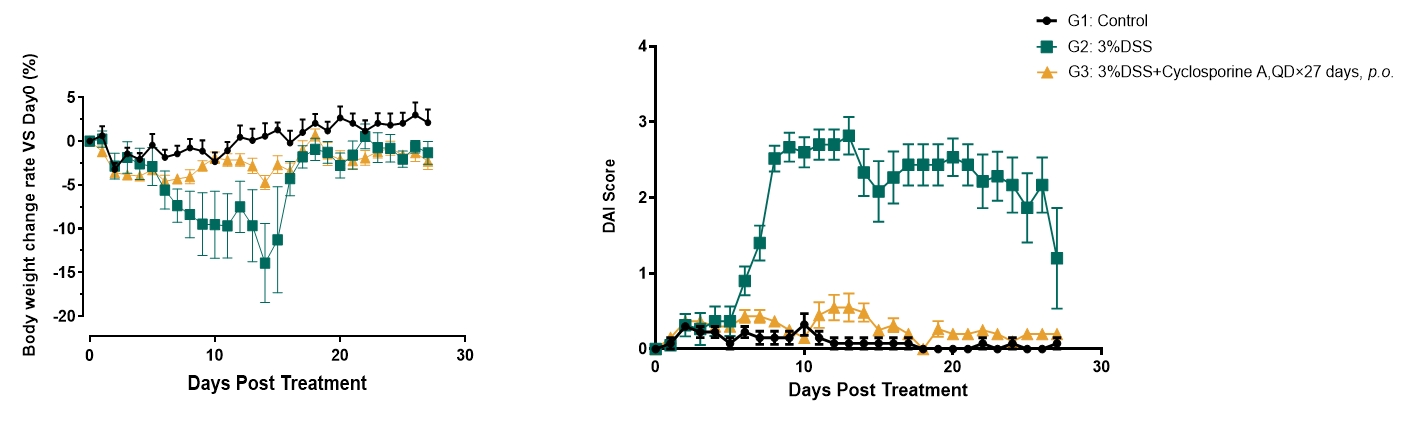
Body weight-loss and DAI score increase were observed in DSS induced model.
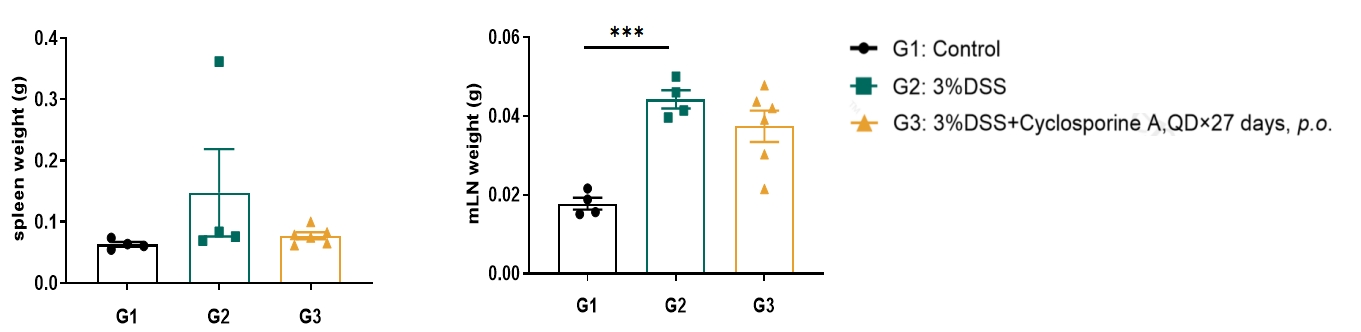
Mesenteric lymph node (mLN) weight increase was observed in DSS induced model.
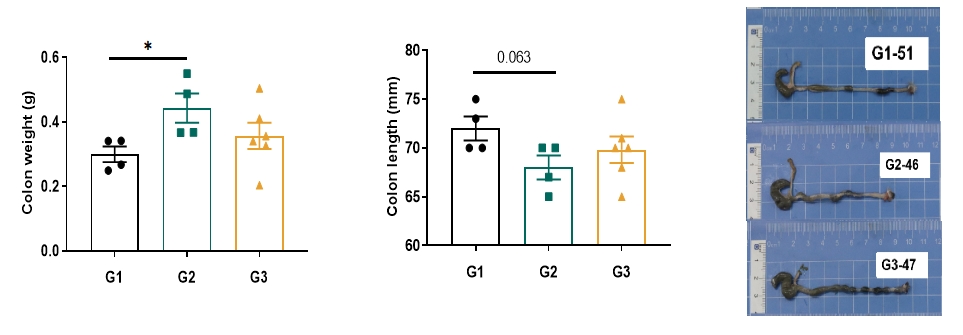
Colon weight increase and length decrease were observed in DSS induced model.
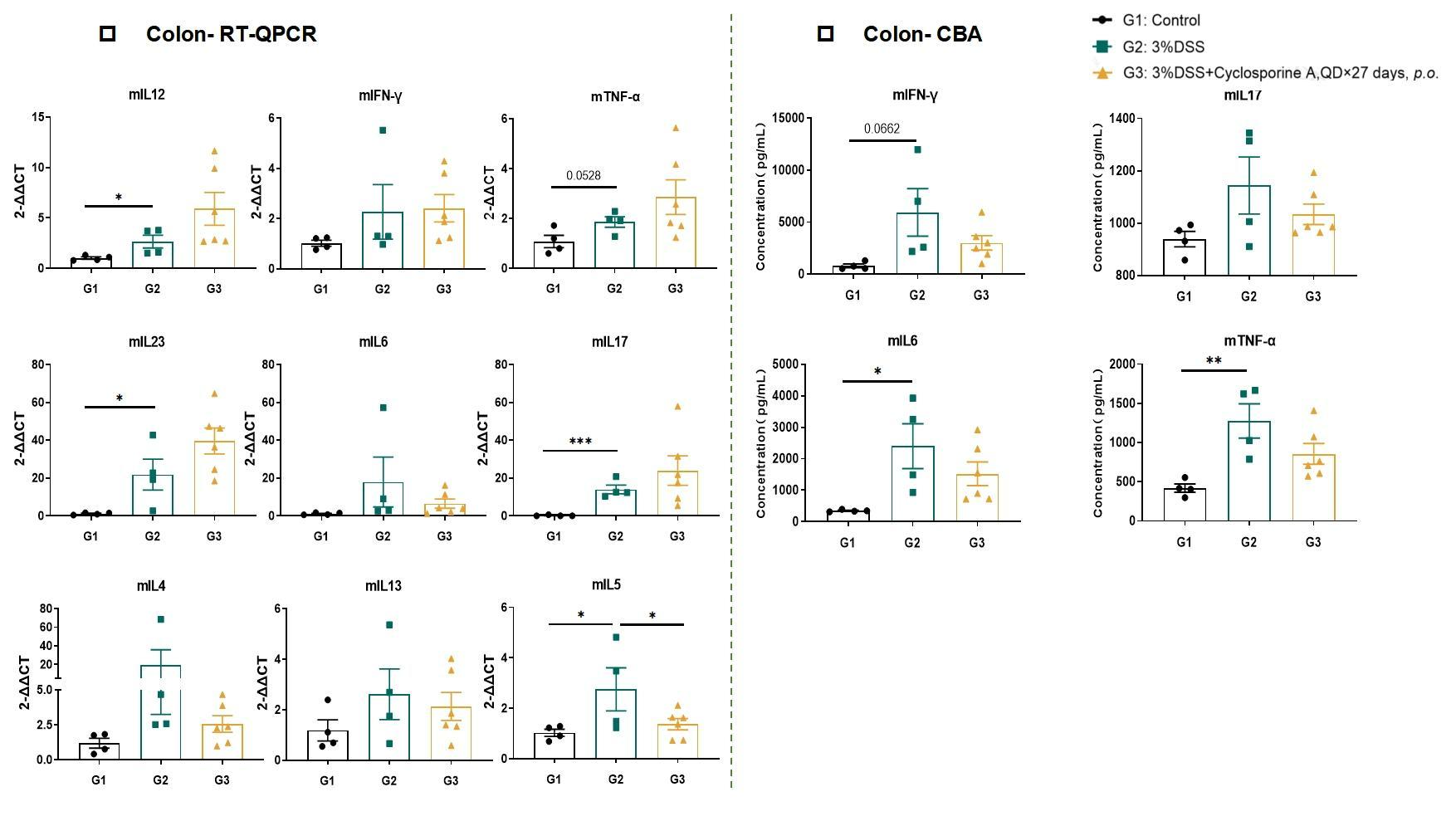
Th1/Th2/Th17 cell involved in DSS induced chronic colitis model,especially Th17 cell.