C3 Glomerulonephritis is a rare kidney disorder characterized by abnormal activation of the complement system, specifically the alternative pathway, leading to deposition of the complement protein C3 predominantly in the glomeruli (kidney filters). It is distinct from immune complex-mediated glomerulonephritis (e.g., IgA nephropathy) due to the absence of significant immunoglobulin deposits.
To aid with your preclinical studies, GemPharmatech has developed and validated several models of C3 glomerulonephritis in mice. They include an anti-glomerular basement membrane (anti-GBM) treated complement factor H (CFH) knockout mouse as well as a C57BL/6J-hC3 mouse model.
Anti-GBM accelerate kidney manifestations of B6-CFH KO
Complement factor H (CFH) is a critical regulator of the complement system and CFH abnormalities have been implicated in diseases such as dense deposit disease, atypical hemolytic syndrome and age related macular degeneration. While CFH knockout mice developed proliferative glomerulonephritis with endocapillary F4/80+ macrophage (Mϕs) infiltration, no significant urinary biochemistry changes was observed in B6-CFH KO until treatment with anti-GBM antibodies.
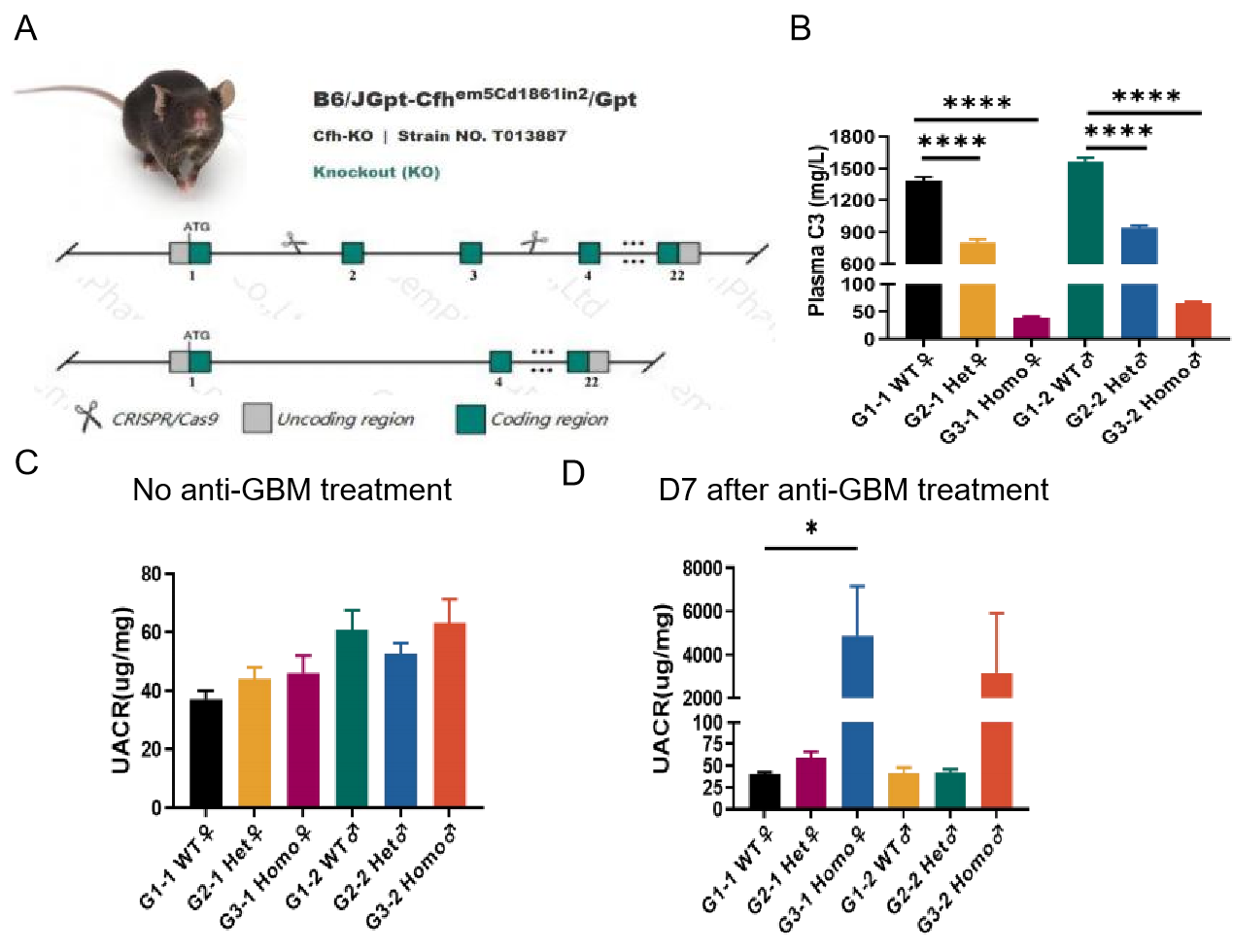
Fig1. anti-GBM on B6-CFH KO present with characteristics of C3 Glomerulonephritis model. A: the model creation strategy of B6-CFH KO; B: C3 levels in the plasma of B6-CFH KO (homozygote and heterozygote) decreased compared with WT mouse; C: Urine Albumin-Creatinine Ratio (UACR) in B6-CFH KO showed no significant increase compared with WT mouse; D: UACR in B6-CFH KO was elevated following anti-GBM treatment compared with WT mouse. Data presented as mean ± SEM. *P<0.05,**P<0.01;***P<0.001.N=8.
C57BL/6J-hC3, a spontaneous C3 Glomerulonephritis mouse model
C3 nephritic factors (C3NF) are a group of autoantibodies that target the C3bBb convertase of the alternative complement pathway. This results in increased C3 activation and are associated with a range of clinical diseases including various nephropathies, partial lipodystrophy and retinal changes as well as infections. In this model, overexpression of human C3 in C57BL/6J mouse was sufficient to induce spontaneous C3 Glomerulonephritis.
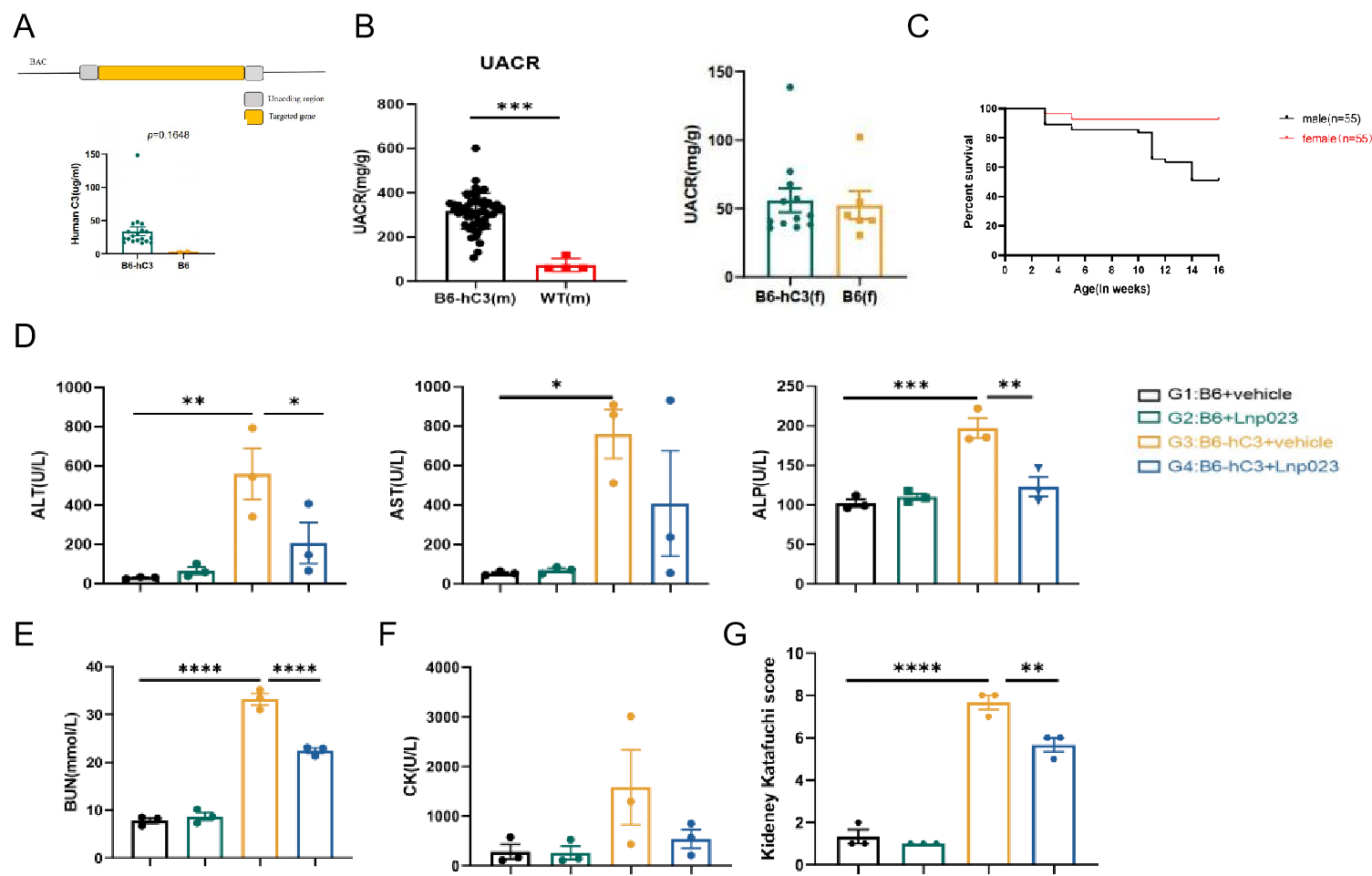
Fig2. C57BL/6J-hC3, a spontaneous C3 Glomerulonephritis mouse model with a high expression of human C3. A: the model strategy of C57BL/6J-hC3 overexpresses human C3 while retaining endogenous mouse C3 (top). Higher serum level of C3 was observed compared to WT mice (bottom). B: UACR was significant raised in male C57BL/6J-hC3 but not in females. C: the survival curve of C57BL/6J-hC3. D: treatment with complement factor B (CFB) inhibitor (Lnp023) relieved the liver damage; E, treatment of CFB inhibitor (Lnp023) reduced BUN accumulation; F, treatment of CFB inhibitor (Lnp023) relieved the heart damage; G, treatment of CFB inhibitor (Lnp023) decreased the kidney inflammation. Data presented as mean ± SEM. *P<0.05,**P<0.01;***P<0.001.