Psoriasis is a chronic immune-mediated skin disorder characterized by erythematous plaques, scaling, and dysregulated keratinocyte proliferation. To address diverse therapeutic development needs, we offer two validated psoriasis models with distinct mechanistic profiles:
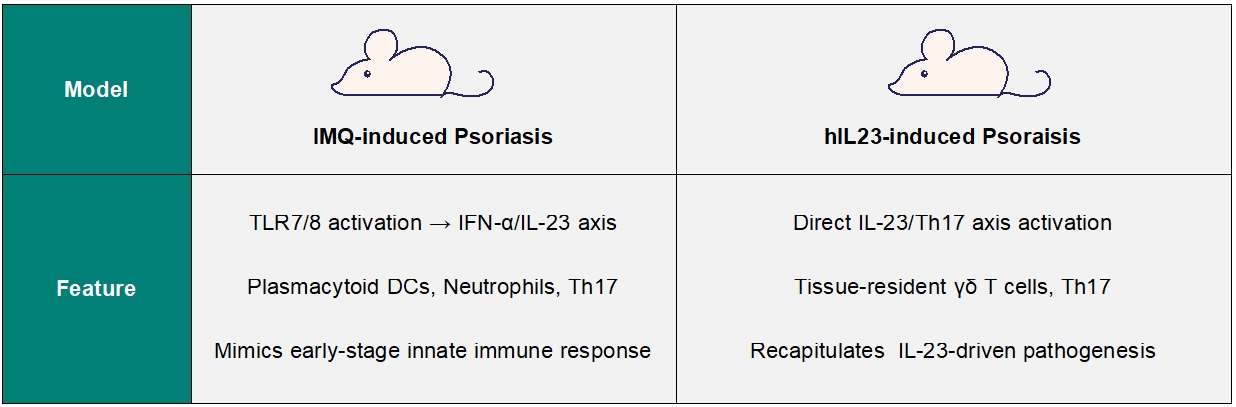
IMQ-induced Psoraisis
Our Imiquimod (IMQ)-induced psoriasis model replicates key human pathology through topical application of IMQ, activating the Th17/IL-23 signaling axis and inducing hallmark psoriatic features within 7 days. This validated model can be used to evaluate novel biologics, small molecules, and gene therapies. Customizable protocols are available for compound efficacy, biomarker discovery, and mechanism-of-action studies.
Technical specifications include histopathological scoring (PASI-like criteria), flow cytometry of skin immune cells, and pathological analysis (HE staining).
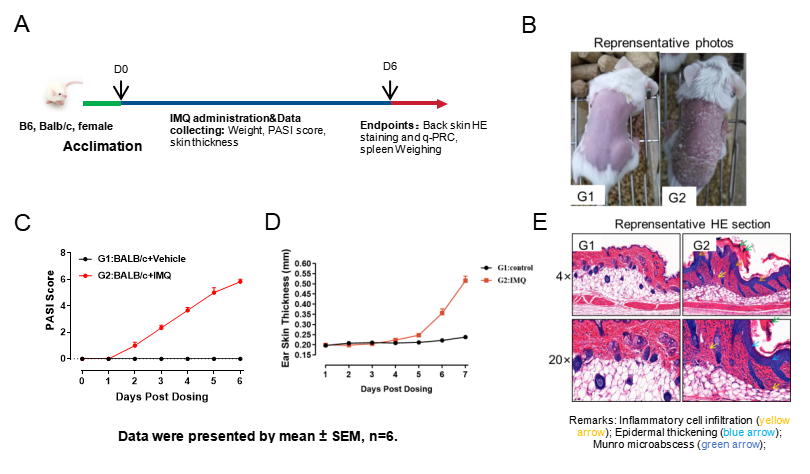
Fig.1 IMQ-induced mouse Psoriasis model
The model strategy of IMQ-induced psoriasis is shown in Fig.1A. After IMQ induction for 6 days, the representative photos of back skin were shown (Fig.1B). PASI score increased in model group, along with thickness of the ear skin (Fig.1C, 1D). Infiltrating inflammatory cells were observed in the dermis of the IMQ-induced psoriasis group. (Fig.1E).
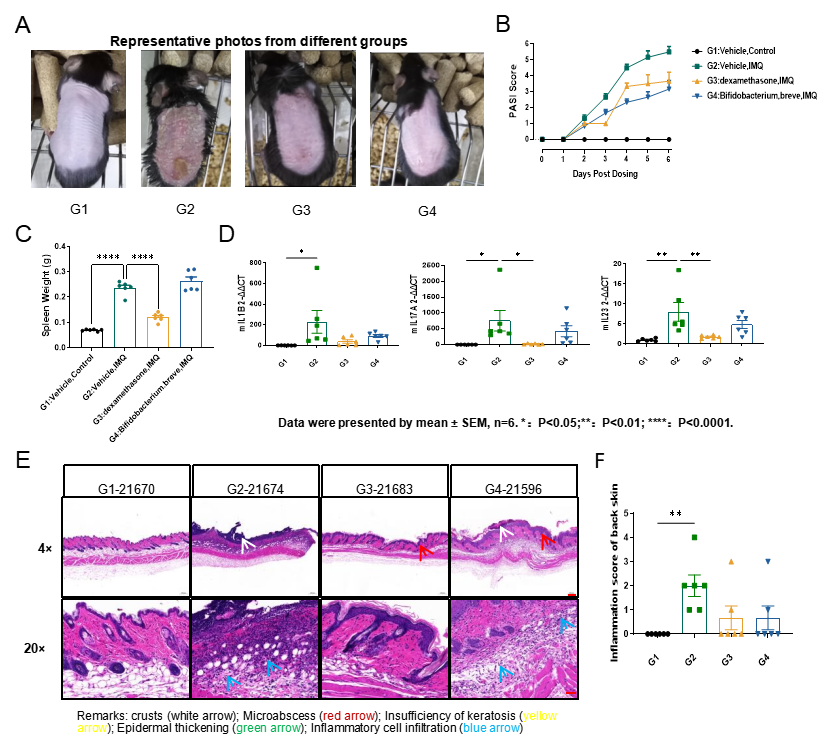
Fig.2 The efficacy study of Dexamethasome and Bifidobacterium in IMQ-induced psoriasis model
The representative photos from different groups were shown in Fig.2A. Treatment with dexamethasome and bifidobacterium reduced PASI score, (Fig.2B) while dexamethasome only treatment inhibited spleen enlargement (Fig.2C). Dexamethasome treatment could inhibit the up-regulation of mouse IL-17A and IL-23 in the skin (Fig.2D). The skin inflammation score exhibited a downward trend following dexamethasome and bififobacterium treatment (Fig.2D&2E).
hIL-23-induced Psoriasis
The hIL-23 Injection Model utilizes the activation of the IL-23/Th17 signaling axis, inducing sustained keratinocyte proliferation and elevated IL-17A, IL-17F expression. This model mirrors human plaque psoriasis with enhanced vascular remodeling and tissue-resident T-cell infiltration, making it suitable for evaluating biologics targeting IL-23p19 or downstream JAK/STAT pathways.
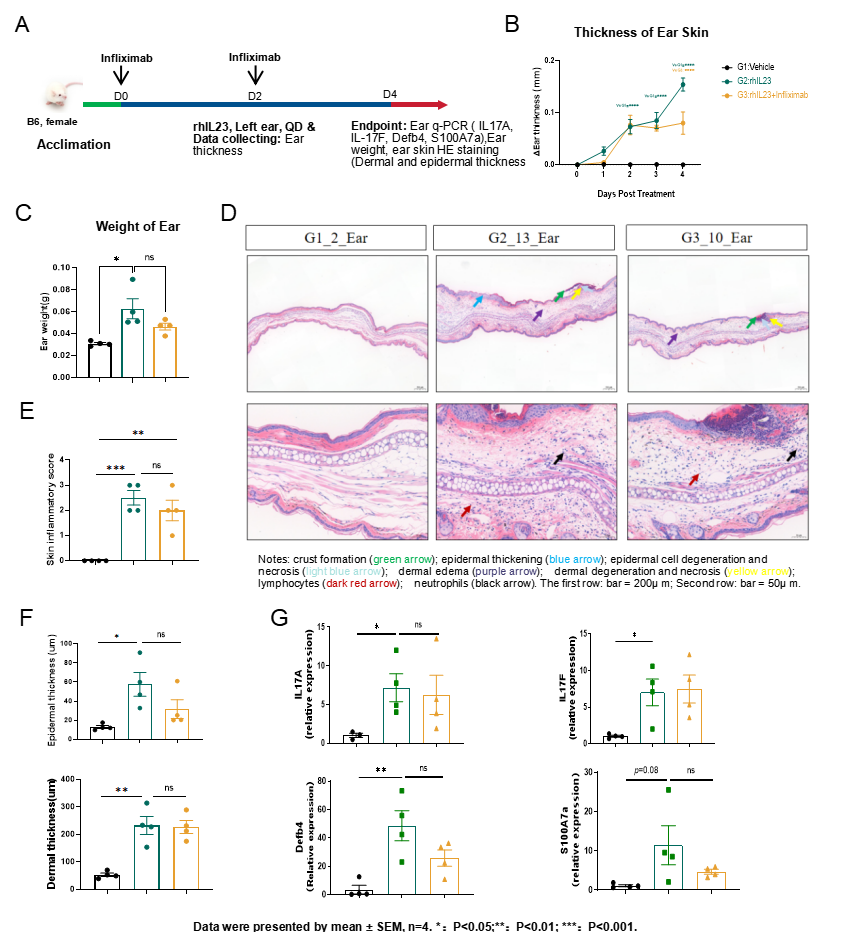
Fig.3 The efficacy study of infliximab in hIL-23-induced psoriasis model
The model strategy of hIL-23-induced psoriasis is shown in Fig.3A. Ear thickness increased after hIL-23 administration and was inhibited following infliximab treatment (Fig.3B). The weight of ear increased significantly after hIL-23 administration (Fig.3C). The inflammatory score of ear skin increased significantly as well as epidermal and dermal thickness (Figure. 3D&3E&3F). hIL-23 administration up-regulated the expression levels of mouse IL-17A, IL-17F, Defb4 and S100A7a in the ear skin (Fig.3G).