Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) has become the most prevalent chronic liver disease worldwide, strongly linked to metabolic syndrome, obesity, type 2 diabetes, and dyslipidemia. The escalating prevalence of metabolic syndrome has led to MASLD and its severe form, Metabolic Dysfunction Associated Steatohepatitis (MASH), becoming a major public health concern, imposing a significant burden on global healthcare systems. While numerous anti-MASLD/MASH agents have entered development pipelines, only Resmetirom (MGL-3196), a THR-β agonist, has been approved by FDA to treat MASH. There remains a high demand for novel therapies in the MASLD/MASH field.
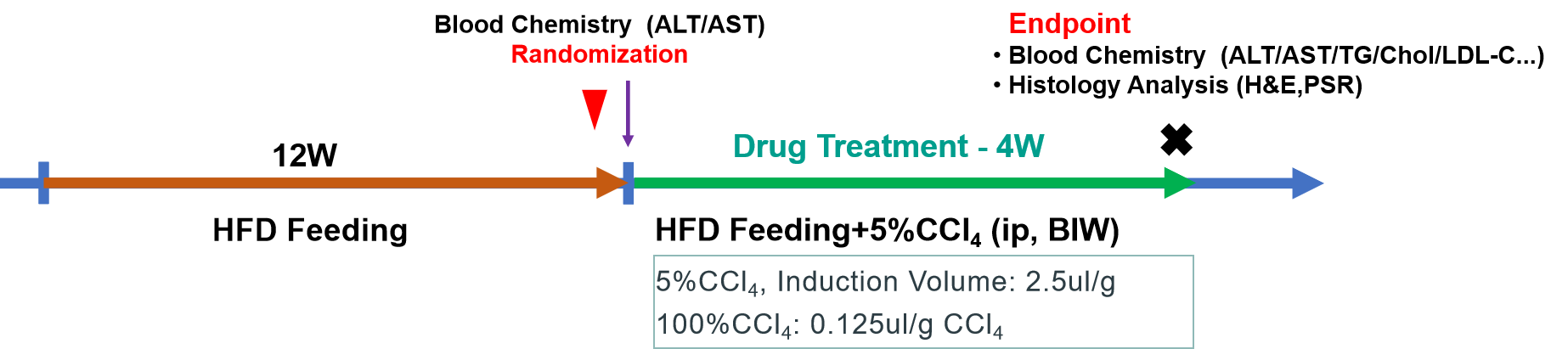
Our previous studies have demonstrated that when C57BL/6 mice are fed a 60% HFD for 12 weeks, they develop symptoms such as obesity and hyperlipidemia. Subsequently, a 4 - week induction with CCl4 can further accelerate liver damage and fibrosis. Thus, we constructed a MASH mouse model induced by HFD+CCl4. The data below demonstrate the efficacy of MGL-3196 in the DIO+CCl4 mouse model, suggesting that this model may be useful for the evaluation of other therapeutics for the treatment of MASLD/MASH.
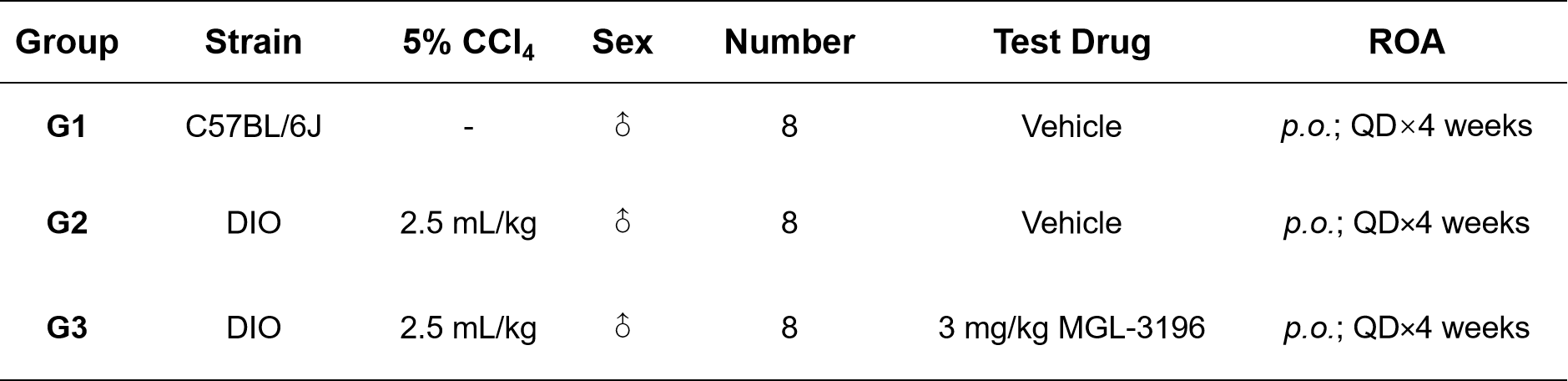
Male DIO mice aged 16-18 weeks, fed a 60% high-fat diet (HFD) for 12 weeks, were randomly grouped based on their plasma ALT level and body weight. During the treatment period, 5% CCl4 was intraperitoneally injected twice per week. Concurrently, the mice were orally administered the MGL-3196 at a dose of 3 mg/kg once a day for 4 weeks. The physiological parameters of body weight, liver enzymes, and blood lipids were monitored in life and the histopathological analysis of liver and liver lipid content were performed at the endpoint.
Example Data
1. Study design
2. MGL-3196 (3mpk) treatment improves metabolic syndrome in DIO+CCl4 model of MASH
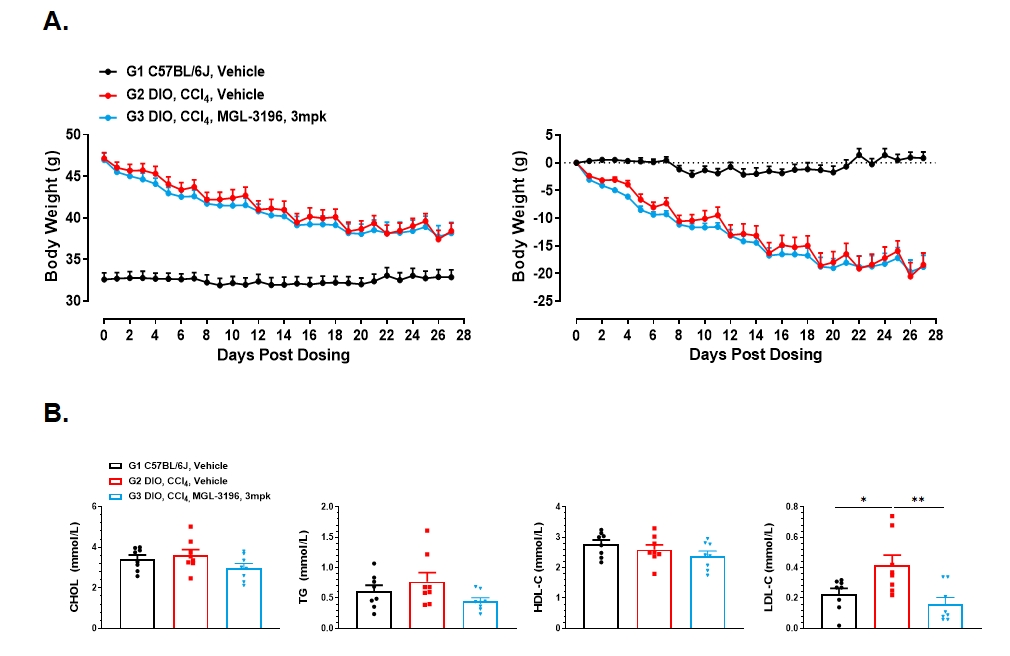
Figure 2. MGL-3196 (3mpk) treatment improves metabolic syndrome in DIO+CCl4 model of MASH. A. Body weight throughout the experimental period. B. Blood lipid was measured at the endpoint. Data presented as Mean±SD. n=8. *: p < 0.05; **: p < 0.01 by one way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc test.
3. MGL-3196 (3mpk) treatment significantly reduced liver injury, liver hypertrophy and liver lipid content in DIO+CCl4 model of MASH
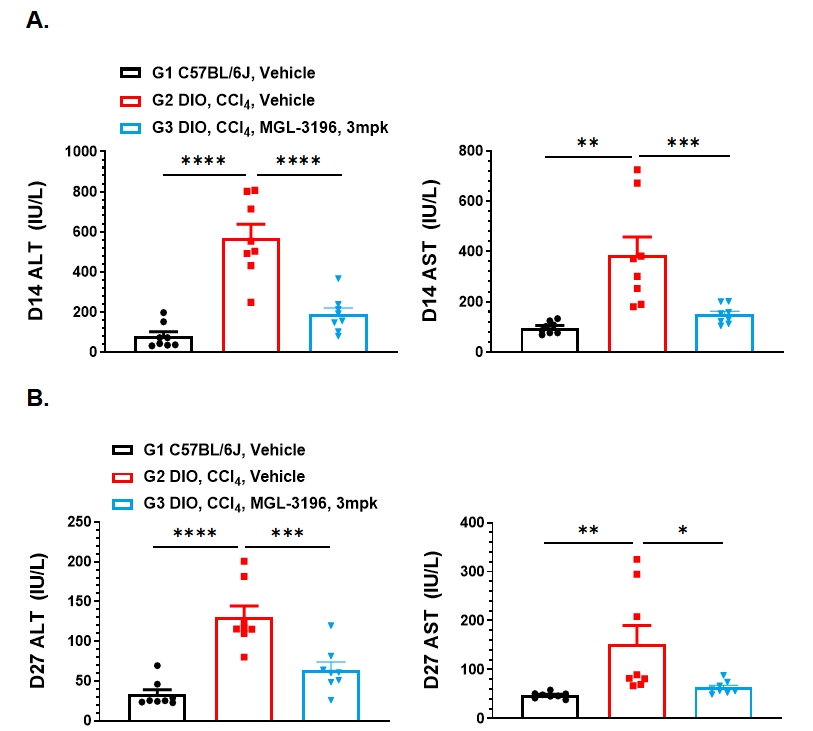
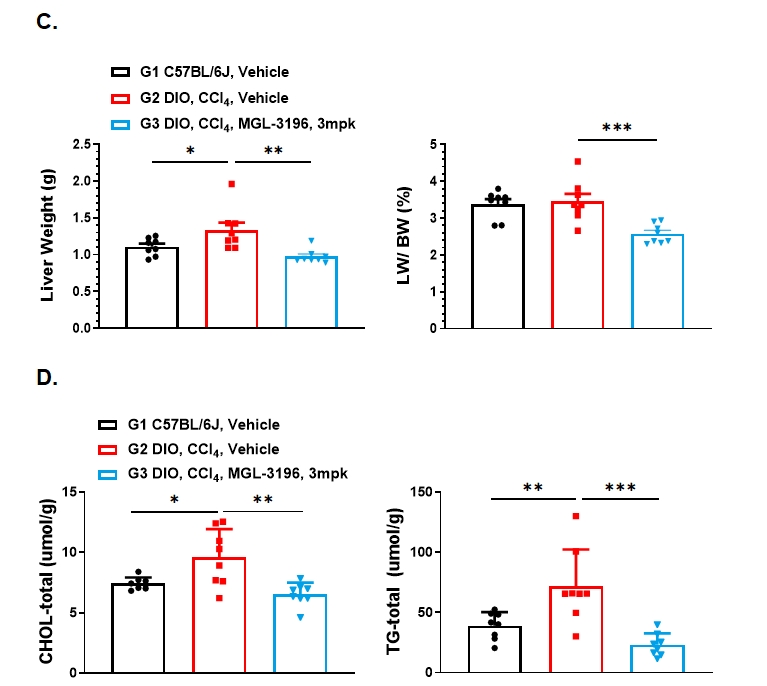
Figure 3. MGL-3196 (3mpk) treatment significantly reduced liver injury, liver hypertrophy and liver lipid content in DIO+CCl4 model of MASH. A. Plasma liver enzymes ALT and AST were detected on Day 14. B. Plasma liver enzymes ALT and AST were detected on Day 27. C. Liver weight and liver organ coefficient at the endpoint. D. Liver triglyceride content was detected at the endpoint. Data presented as Mean±SD. n=8. **: p < 0.01; ***: p < 0.001; ****: p < 0.0001 by one way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc test.
4. MGL-3196 (3mpk) treatment decreased NAFLD activity score in DIO+CCl4 model with no significant effect on liver fibrosis
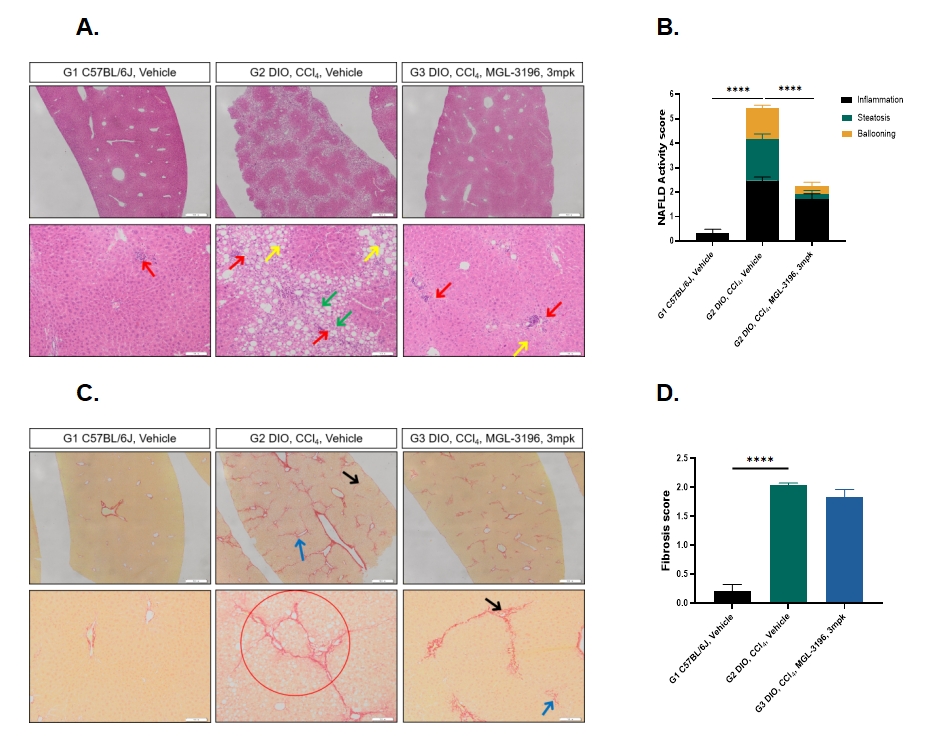
Figure 4. MGL-3196 (3mpk) treatment decreased NAFLD activity score in DIO+CCl4 model with no significant effect on liver fibrosis. A and B. H&E staining and NAFLD Activity Scores, Scale bar = 100 μm (upper panel), 50 μm (bottom panel). C and D. Sirius Red staining and fibrosis scores. Scale bar = 100 μm (upper panel), 50 μm (bottom panel). Data presented as Mean±SD. n=8. ****: p < 0.0001 by one way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc test.
Our research findings indicated that after the DIO mice received CCl₄ injections, there was an upward trend in blood lipid levels, liver fat content, liver enzyme levels, and liver weight. Liver pathology results suggested further damage to the liver tissue. After being treated with MGL-3196 (3 mg/kg), there were significant average decreases in blood lipid levels, liver fat content, liver enzyme levels, and liver weight of the mice. Meanwhile, the NAFLD activity score of the mice also showed a significant downward trend, yet it had no obvious impact on the fibrosis process. Consequently, the DIO+CCl4 model could serve as a valuable model for pre-clinical studies of anti-MASH agents.