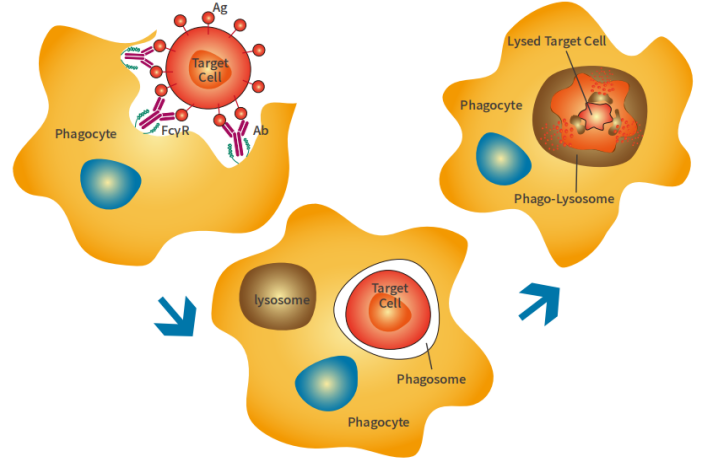
Antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis (ADCP) is a process in which immune cells engulf target cells in the presence of antibodies. This process is initiated when the Fab end of the antibody binds to a ligand on the target cell's surface, and the Fc end of the antibody binds to FcγR on the phagocyte's surface. This interaction triggers a series of second messenger responses, resulting in the engulfment of the target cell by the phagocyte. The FcγR-mediated engulfment process not only helps fight infections but also plays a crucial role in cancer treatment.
Case:Rituximab- induced ADCP effect detection.
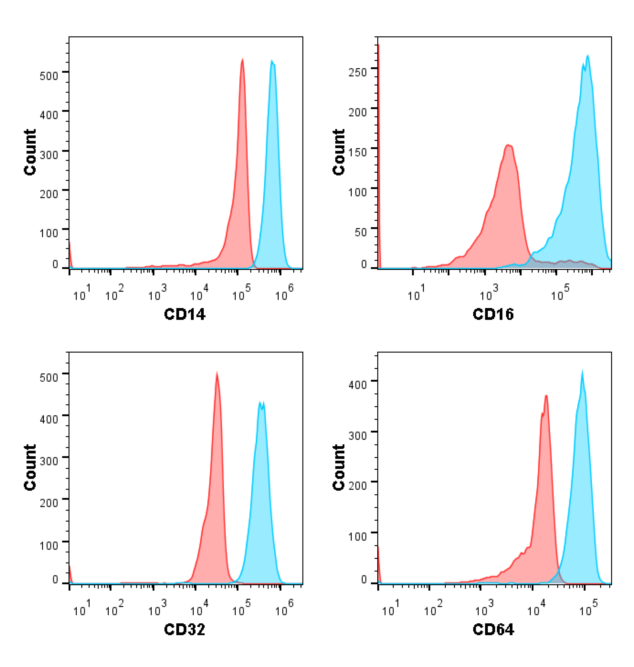
Fig. Flow detection results of macrophages induced by monocytes derived from PBMC in vitro.
Using two different fluorescent dyes to label target cells and macrophages. After the macrophages ingest the target cells, they emit a double-positive signal (located in Stream graph Q2 quadrant).
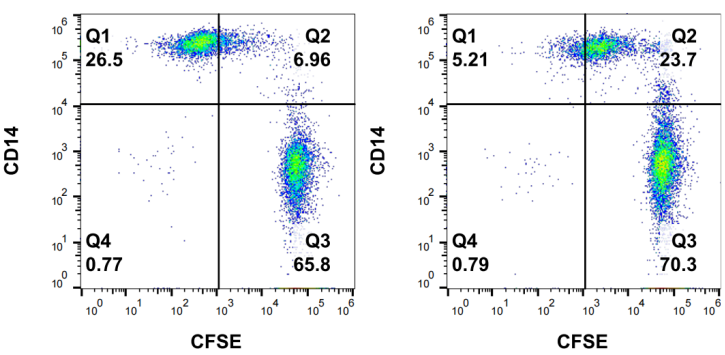
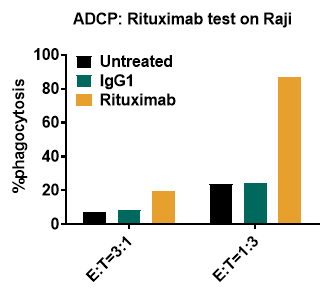
Fig. Rituximab Mediated phagocytosis (ADCP)
GemPharmatech Advantages
Extensive library of target cells (300+ cancer cell lines and humanized cell lines) and qualified BSL-2 level laboratories.
Providing free comparator antibody therapy for common viral infections.
Evaluating the effect of signal activation in a simulated genetic cell system (Jurkat-CD32a-NFAT-luc) for early screening of antibody drugs.
Analysis of M1/M2-type giant cell-derived ADCP effect.
Establishing sufficient QC detection standards for the differentiation and maturation of macrophages.
Extensive project experience.
Meeting the regulatory requirements for new drug application submissions.
Strict laboratory data storage standards ensure experiment traceability.