T cell immunoglobulin and ITIM domain (TIGIT) is a type I transmembrane protein with an immunoglobulin (Ig) domain at its extracellular region and an ITIM domain at its intracellular region and is mainly expressed on the surface of T-cells and NK-cells. Previous research demonstrated that the deletion of TIGIT would result in enhanced T-cell response to MOG peptide fragment vaccination, suggesting that TIGIT was a T-cell inhibitory receptor.
It is believed that T cell inhibition by TIGIT can occur either through the direct action of TIGIT on T cells, which weakens T cell signaling by down-regulating the TCR-α chain, thereby inhibiting T cell activation[1]; or through the activation of the downstream signaling channel of PVR ligand on APC, which increases ERK phosphorylation and the secretion of anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 from APC. IL-10, in turn, acts on T cells, thereby inhibiting the T-cell response[2]. TIGIT antibodies, alone or in combination with PD-L1 antibodies, may be used to treat advanced or metastatic cancers.
Development strategy
GemPharmatech has developed TIGIT humanized mouse models, including single-target models, such as BALB/c-hTIGIT and C57BL/6-hTIGIT, double-target models, such as BALB/c-hPD1/hTIGIT and C57BL/6-hPD1/hTIGIT, and triple-target models, such as BALB/c-hPD1/hPDL1/hTIGIT. In all models, TIGIT humanization was done by replacing the extracellular region of TIGIT from BALB/c and C57BL/6 mice with the corresponding human gene segments, while keeping the intracellular region of murine TIGIT protein intact. TIGIT humanized mouse models are excellent animal models for efficacy evaluation of human TIGIT inhibitors.
1. BALB/c-hTIGIT and C57BL/6-hTIGIT: hTIGIT antibody drug efficacy test
BALB/c-hTIGIT mice were subcutaneously inoculated with CT26.WT tumor cell line, and B6-hTIGIT mice were subcutaneously inoculated with MC38 tumor cell line to investigate the inhibitory effects of anti-human TIGIT antibodies on tumor growth.
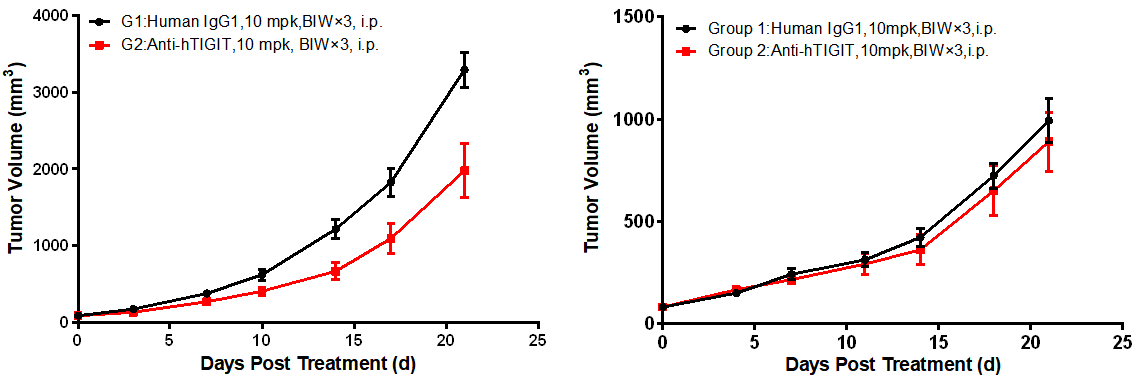
Left figure: In vivo efficacy evaluation in BALB/c-hTIGIT mice. Right figure: In vivo efficacy evaluation in B6-hTIGIT mice
Comparative study on in vivo efficacy in BALB/c-hTIGIT and B6-hTIGIT mice. BALB/c-hTIGIT and B6-hTIGIT mice were subcutaneously inoculated with colon cancer CT26.WT cells and MC38 cells, respectively. When the mean tumor volume reached approximately 80 - 120 mm3, the mice were randomly divided into the Control Group or Anti-hTIGIT Monotherapy Group (n = 10) which were treated twice a week with six doses in total. The data are presented as Mean ± SEM.
The results showed an excellent anti-tumor effect in BALB/c-hTIGIT mice inoculated with CT26.WT tumor cells when treated with anti-human TIGIT antibody (TGI = 40.26%), while no tumor inhibition effect was observed in B6-hTIGIT mice inoculated with MC38 tumor cells after treatment with anti-human TIGIT antibody (TGI = 12.03%).
The results demonstrated that compared with the B6-hTIGIT mouse model inoculated with MC38 cells, the anti-hTIGIT antibody yielded statistically significant efficacy in the BALB/c-hTIGIT model inoculated with CT26.WT cells, suggesting that the BALB/c-hTIGIT mouse model is a better model for efficacy evaluation of anti-human TIGIT antibodies.
2.BALB/c-hPD1/hTIGIT and C57BL/6-hPD1/hTIGIT: hTIGIT antibody drug efficacy test
BALB/c-hPD1/hTIGIT mice were subcutaneously inoculated with CT26.WT tumor cell line, and B6-hPD1/hTIGIT mice were subcutaneously inoculated with MC38 tumor cell line to investigate the inhibitory effects of anti-human TIGIT antibodies on tumor growth.
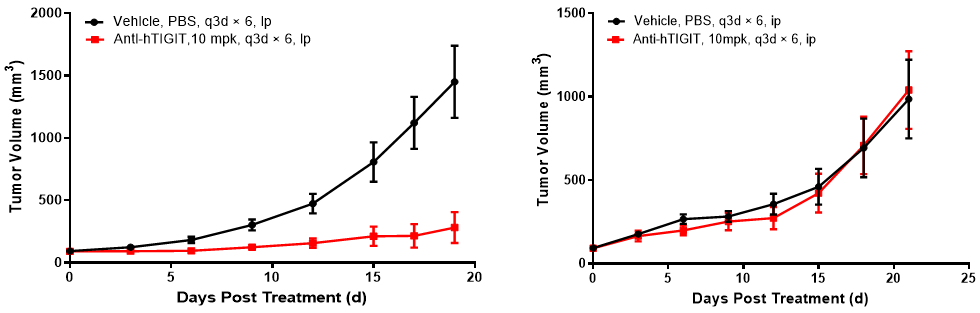
Left figure: In vivo efficacy evaluation in BALB/c-hPD1/hTIGIT mice. Right figure: In vivo efficacy evaluation in B6-hPD1/hTIGIT mice
Comparative study of in vivo efficacy in BALB/c-hPD1/hTIGIT and B6-hPD1/hTIGIT mice. BALB/c-hPD1/hTIGIT and B6-hPD1/hTIGIT mice were subcutaneously inoculated with colon cancer CT26.WT cells and MC38 cells respectively. When the mean tumor volume reached approximately 80 - 120 mm3, the mice were randomly divided into the Control Group or Anti-hTIGIT Monotherapy Group (n = 6) which were treated twice a week with six doses in total. The data are presented as Mean ± SEM.
Results: Good anti-tumor effect was observed in BALB/c-hPD1/hTIGIT mice inoculated with CT26.WT tumor cells after treatment with anti-human TIGIT antibody (TGI = 79%), while no tumor inhibition effect was observed in B6-hPD1/hTIGIT mice inoculated with MC38 tumor cells after treatment with anti-human TIGIT antibody. Compared with the B6-hPD1/hTIGIT mouse model inoculated with MC38 cells, the anti-hTIGIT antibody yielded statistically significant efficacy in the BALB/c-hPD1/hTIGIT model inoculated with CT26.WT cells.
The results demonstrated that the BALB/c-hPD1/hTIGIT mouse model is a better model for efficacy evaluation of anti-human TIGIT antibodies.
3.BALB/c-hPD1/hTIGIT: Keytruda, Triagolumab and M Triagolumab drug efficacy test
BALB/c-hPD1/hTIGIT mice were subcutaneously inoculated with CT26.WT tumor cell line to investigate the tumor inhibition effect of Keytruda (an anti-human PD1 antibody), Triagolumab and M Triagolumab.
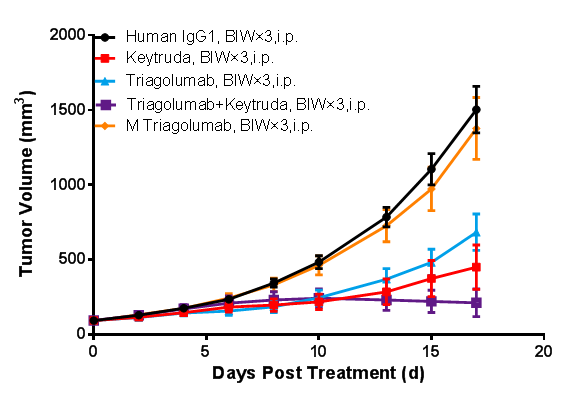
(Data from verification studies by third-party partners)
In vivo efficacy study in BALB/c-hPD1/hTIGIT mice. BALB/c-hPD1/hTIGIT mice were subcutaneously inoculated with colon cancer CT26.WT cells. When the mean tumor volume reached approximately 80 - 120 mm3, the mice were randomly divided into Human IgG1 Group, Keytruda Monotherapy Group, Tiragolumab Monotherapy Group, M Tiragolumab Monotherapy Group, and Keytruda + Tiragolumab Combination Therapy Group (n = 8). They were dosed twice a week for six doses in total. The data are presented as Mean ± SEM.
The results showed that tumor growth inhibition (TGI) results were 56.79% and 75.34%, respectively, in the Keytruda Group and Tiragolumab Group, suggesting inhibitory effects on tumor growth. Enhanced tumor inhibition was observed in the Keytruda + Tiragolumab Combination Therapy Group, with a TGI of 88.94%. M Tiragolumab was developed through mutation in the Fc domain of Tiragolumab to eliminate Tiragolumab-mediated ADCC (antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity). It wasn’t able to effectively inhibit tumor growth (TGI = 10.04%).
The results demonstrated that the BALB/c-hPD1/hTIGIT mouse model is an appropriate animal model for screening and evaluating monotherapies and combination therapies of PD1 and TIGIT humanized antibodies. It can also be used for assessing the ADCC of antibody-based drugs.
References:
[1] Joller, Nicole, et al. "Cutting edge: TIGIT has T cell-intrinsic inhibitory functions." The Journal of Immunology 186.3 (2011): 1338-1342.
[2] Stanietsky, Noa, et al. "The interaction of TIGIT with PVR and PVRL2 inhibits human NK cell cytotoxicity." Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 106.42 (2009): 17858-17863.

