(BALB/c-hCTLA4, C57BL/6-hCTLA4, BALB/c hPD1/ hCTLA4, C57BL/6- hPD1/ hCTLA4)
Cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen-4 (CTLA4), also known as CD152, is an immunoglobulin superfamily-related cluster of differentiation encoded by the CTLA4 gene. Its extracellular domain is the receptor/ligand-binding domain, while its cytoplasmic domain is crucial for signaling.
Regulatory T (Treg)-cells are a subset of T-cells that primarily express CTLA4 and are able to inhibit cell-mediated immunity. Currently, it is believed that CTLA4 regulates the functional placement of Treg. CTLA4 possesses an extracellular domain that can compete with CD28 for binding to B7 molecule ligands (CD80/CD86) on the surface of antigen-presenting cells (APCs). This interaction generates inhibitory signals that prevent T-cell activation, shielding tumor cells from T-lymphocyte attack. Due to this effect, locking the immunological action of CTLA4 should potentially be able to induce the proliferation of immunocytes, hence triggering or strengthening the antitumor immune response [1-2].
Development Strategy:
GemPharmatech has created multiple CTLA4 humanized mouse models, including single-humanized BALB/c-hCTLA4, C57BL/6-hCTLA4 mice, and double-humanized BALB/c-hPD1/hCTLA4 and C57BL/6-hPD1/hCTLA4 mice, by using gene editing techniques to replace the CTLA4 extracellular domain of BALB/c and C57BL/6 mice with a corresponding human fragment. CTLA4 humanized mice models are useful for evaluating the effectiveness and safety of human CTLA4 inhibitors.
1. BALB/c-hCTLA4: YERVOY® Drug Efficacy Test
The tumor inhibitory efficacy of YERVOY® (Ipilimumab), an anti-human CTLA4 antibody, was tested in BALB/c-hCTLA4 mouse models subcutaneously transplanted with CT26.WT tumor cell line.
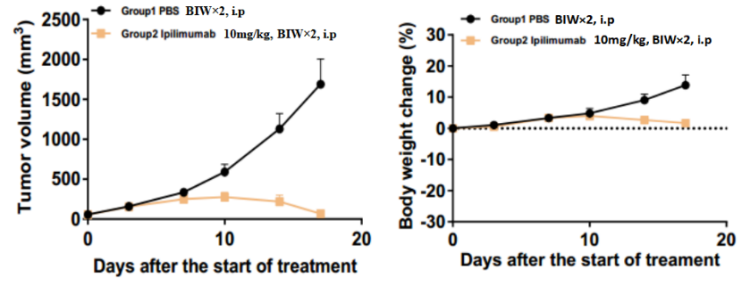
Left Figure: Mouse tumor growth curve Right Figure: Mouse body weight curve
(Data from a third-party source)
BALB/c-hCTLA4 humanized mice were subcutaneously transplanted with murine colon cancer cells CT26.WT. When tumors reached an average volume of about 100 mm3, the mice were randomized to either the Control Group or the Treatment Group (n = 7) and treated with drugs at corresponding dosages. The drugs were administered twice a week for a total of 4 doses. The data are presented as Mean ± SEM.
Results: The anti-human CTLA4 antibody Yervoy had a very significant inhibitory effect on tumor growth.
The results demonstrated the BALB/c-hCTLA4 mouse is a powerful instrument for evaluating the in vivo efficacy of human CTLA4 antibodies.
2. BALB/c-hCTLA4: YERVOY® Pharmaceutical Dosage Validation
The dose-response relationship of tumor inhibition of YERVOY® (Ipilimumab), an anti-human CTLA4 antibody, was tested in a model of BALB/c-hCTLA4 mice subcutaneously inoculated with the CT26.WT tumor cell line.
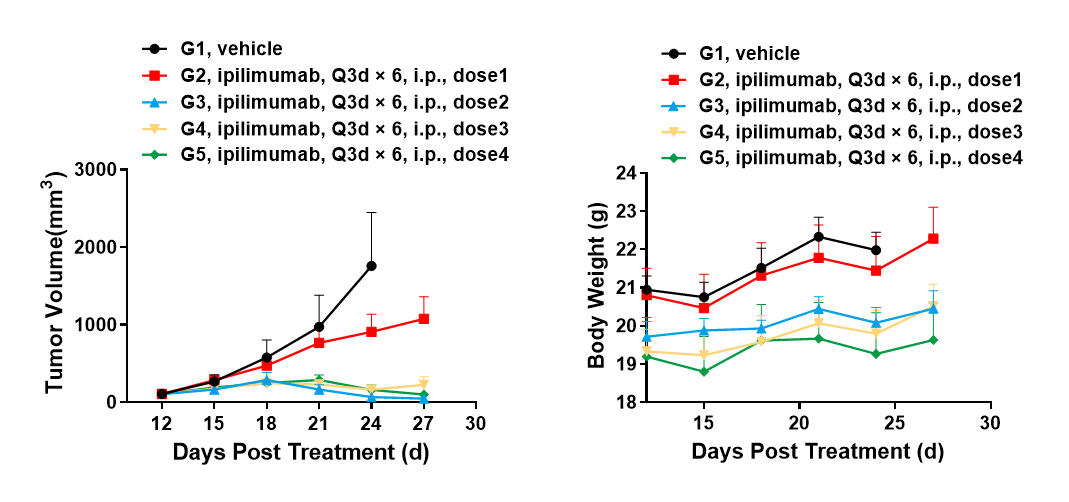
Left Figure: Mouse tumor growth curve Right Figure: Mouse body weight curve
BALB/c-hCTLA4 humanized mice were subcutaneously transplanted with murine colon cancer cells CT26.WT. When tumors reached an average volume of about 100 mm3, the mice were randomized to the Control Group (G1) or any treatment group (G2-G5). The data are presented as Mean ± SEM.
Results: The anti-human CTLA4 antibody Yervoy showed a very significant inhibitory effect on tumor growth in high-dose treatment groups (G3: TGI = 96%; G4: TGI = 91%; G5: TGI = 87.5%) and specific antitumor efficacy (TGI = 39.6%) in the low-dose treatment group.
The results demonstrate that the BALB/c-hCTLA4 mouse is a powerful instrument for evaluating the in vivo efficacy of human CTLA4 antibodies.
3. C57BL/6-hCTLA4: YERVOY® efficacy test
The tumor inhibitory efficacy of YERVOY® (Ipilimumab) was tested in B6-hCTLA4 mouse models subcutaneously transplanted with CT26.WT tumor cell line.
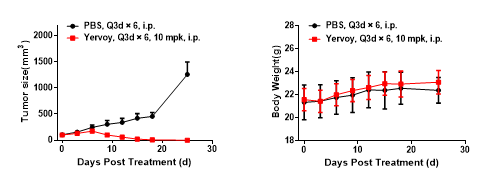
Left Figure: Mouse tumor growth curve Right Figure: Mouse body weight curve
B6-hCTLA4 humanized mice were subcutaneously transplanted with murine colon cancer cells MC38. When tumors reached an average volume of about 100 mm3, the mice were randomized to the Control Group or the Treatment Group (n = 5 for the Control Group; n = 7 for the Treatment Group) and treated with drugs at corresponding dosages. The drugs were administered every three days for a total of 6 doses. The data are presented as Mean ± SEM.
Results: The anti-human CTLA4 antibody Yervoy had a very significant inhibitory effect on tumor growth (TGI = 100%).
The B6-hCTLA4 mouse is an ideal animal model for evaluating the in vivo efficacy of the hCTLA4 antibody.
4. C57BL/6-hCTLA4: YERVOY® pharmaceutical dosage validation
The dose-response relationship of tumor inhibition of YERVOY® (Ipilimumab), was tested in B6-hCTLA4 mouse models subcutaneously inoculated with MC38 tumor cell line.
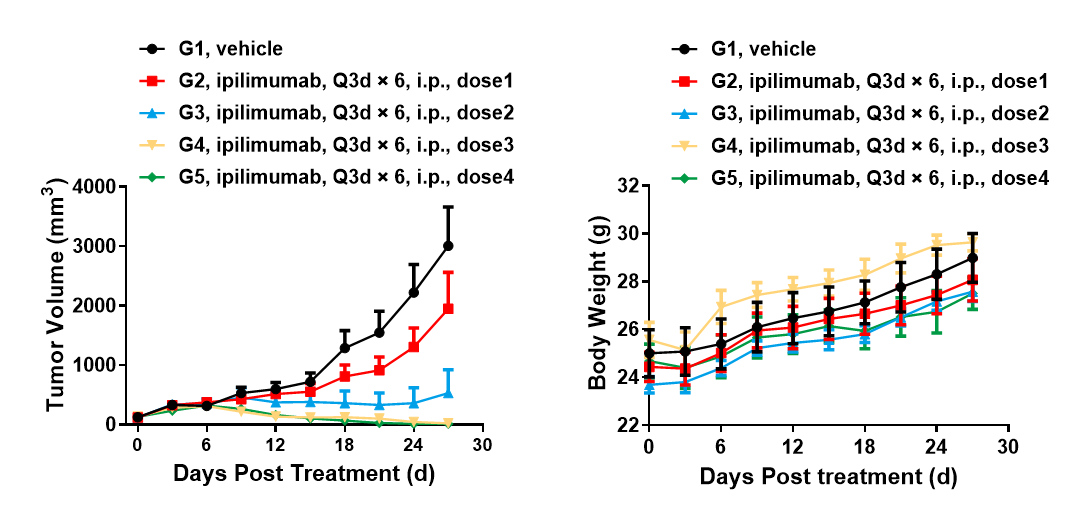
Left Figure: Mouse tumor growth curve Right Figure: Mouse body weight curve
B6-hCTLA4 humanized mice were subcutaneously inoculated with murine colon cancer cells MC38. When tumors reached an average volume of about 100 mm3, the animals were enrolled in the Control Group (G1, N = 6) or any treatment group (G2-G3, N = 6; G4-G5, N = 5). The data are presented as Mean ± SEM.
Results: The anti-human CTLA4 antibody Yervoy showed a significant inhibitory effect on tumor growth in high-dose treatment groups (G3: TGI = 85%; G4: TGI = 99%; G5: TGI = 99%) and specific antitumor efficacy (TGI = 22%) in the low-dose treatment group.
The results show that the B6-hCD137 mouse is a powerful instrument for evaluating the in vivo efficacy of human CTLA4 antibodies.
5. BALB/c-hPD1/hCTLA4: Antitumor Drug Efficacy Test
The tumor inhibitory effect of the anti-human CTLA4 antibody YERVOY® (Ipilimumab) and anti-human PD1 antibody KERTRUDA® was tested in BALB/c-hPD1/hCTLA4 mice subcutaneously transplanted with CT26.WT tumor cell line.
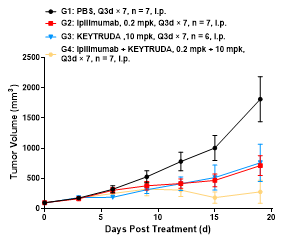
Mouse tumor growth curve
Colon cancer cells CT26.WT in the logarithmic growth phase were subcutaneously inoculated into 6-8 WO BALB/c-hPD1/hCTLA4 humanized mice. When tumors reached an average volume of about 100 mm3, the mice were randomized to PBS Group, Ipilimumab Monotherapy Group, Monotherapy Group, or Ipilimumab + Keytruda Combination Therapy Group (n = 7) and treated with the corresponding drugs. The drugs were administered every three days for a total of 7 doses. The data are presented as Mean ± SEM.
Results: The tumor growth inhibition (TGI) was 59.38% and 50.52%, respectively, in Ipilimumab Monotherapy Group and Keytruda Monotherapy Group; 87.45% in Ipilimumab + Keytruda Combination Therapy Group; significant inhibition of tumor growth was observed in all study groups.
The results demonstrated that the BALB/c-hPD1/hCTLA4 mouse is an ideal animal model for evaluating the antitumor efficacy of humanized CTLA4 antibodies, PD-1 antibodies, and their combination therapies.
6. C57BL/6-hPD1/hCTLA4: antitumor drug efficacy test
The tumor inhibitory effect of the anti-human CTLA4 antibody YERVOY® (Ipilimumab) and anti-human PD1 antibody Opdivo® was tested in B6-hPD1/hCTLA4 mice subcutaneously inoculated with M38 tumor cell line.
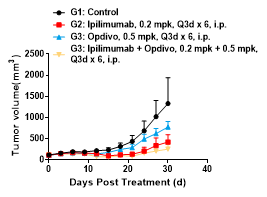
Mouse tumor growth curve
Colon cancer cells MC38 in the logarithmic growth phase were subcutaneously inoculated into 6-8 WO B6-hPD1/hCTLA4 humanized mice. When tumors reached an average volume of about 100 mm3, the mice were randomized to Control Group, Ipilimumab Group, Opdivo Group, or Ipilimumab + Opdivo Combination Therapy Group (n = 5) and treated with the corresponding drugs. The drugs were administered every three days for a total of 6 doses. The data are presented as Mean ± SEM.
Results: The tumor growth inhibition (TGI) was 42.10%, 69.77%, and 87.19%, respectively, in the Ipilimumab Group, Opdivo Group, and Ipilimumab + Opdivo Combination Therapy Group. Certain inhibition was observed in the monotherapy and combination therapy groups, with the combination therapy group showing a stronger antitumor effect.
These results revealed that the B6-hPD1/hCTLA4 mouse is an ideal animal model for assessing the anticancer efficacy of humanized CTLA4 antibody, PD-1/PD-L1 antibody monotherapies, and combination treatments and bispecific antibody therapies.
References
[1] Therapeutic use of anti-CTLA-4 antibodies. Int Immunol. 2015, 27(1):3-10.
[2] Blockade of CTLA-4 on both effector and regulatory T cell compartments contributes to the antitumor activity of anti‒CTLA-4 antibodies. J Exp Med. 2009,3;206(8):1717-25.

