OX40, also known as Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor Superfamily Member 4, TNFRSF4, or CD134, is a receptor molecule essential to the TNFR/TNF superfamily. Research confirms the vital role OX40 plays in CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell mediated immune responses by demonstrating its effect on T-cell-dependent proliferation and differentiation of B-cells. It additionally inhibits apoptosis by promoting the expression of apoptosis inhibitors BCL2 and BCL2lL1/BCL2-XL. Clinical trials showcase how OX40 agonists could promote immunological effects and memory functions, as well as reduce the quantity of immunosuppressive regulatory T-cells, which are primarily found in tumors. Due to its effects, the role of OX40 agonists in cancer treatment is attracting increasing attention; presently, several agonists are either under development or already in use for the treatment of cancers in clinical trials [1-5].
Development Strategy
GemPharmatech has successfully developed humanized OX40 mouse models, including single target-humanized mice BALB/c-hOX40 and C57BL/6-hOX40, and double target-humanized mice C57BL/6-hPD1/hOX40 and BALB/c-hPD1/hOX40, allowing the expression of humanized OX40 to be controlled by the mouse promotor and regulatory sequence.
1. C57BL/6-hOX40: MOXR0916 Analog Drug Efficacy Test
The tumor inhibitory effect of an analog of MOXR0916, an anti-human OX40 antibody, was tested in a model of C57BL/6-hOX40 mice subcutaneously inoculated with MC38 tumor cell line.
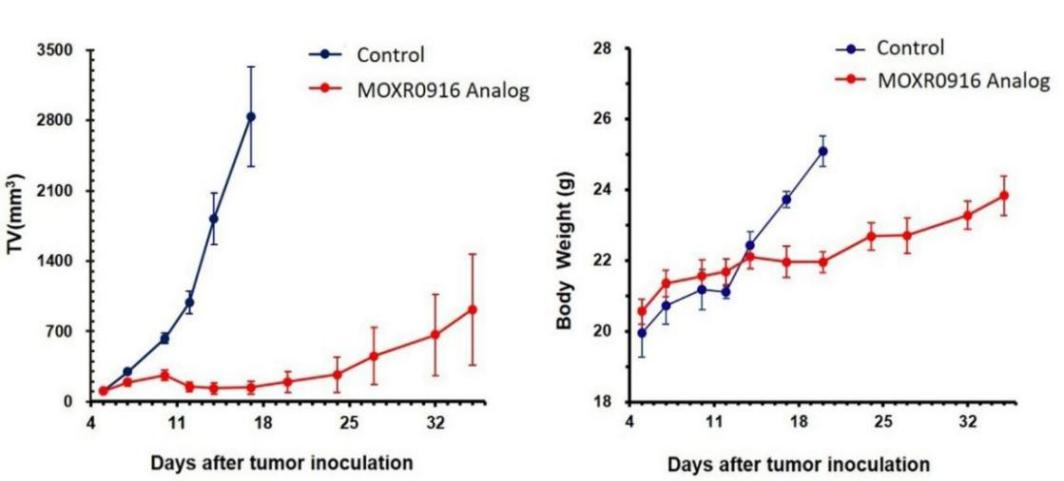
Left Figure: Mouse tumor growth curve Right Figure: Mouse body weight curve
(Data from verification studies by third-party partners)
In vivo efficacy test in a model of B6-hOX40 mice subcutaneously inoculated with MC38. Colon cancer cells MC38 in the logarithmic growth phase were subcutaneously inoculated into 6-8 WO B6-hOX40 humanized mice. When tumors reached an average volume of about 100 mm3, the mice were randomized to Vehicle Group or MOXR0916 Analog Treatment Group (n = 7) and treated with the corresponding drugs. The data are presented as Mean ± SEM.
Results: The administration of MOXR0916 analog showed significant inhibition of tumor growth.
The data shows the B6-hOX40 mouse is an ideal model for evaluating in vivo efficacy of human OX40 antibodies.
2. BALB/c-hPD1/hOX40: anti-hOX40 Drug Efficacy Test
The tumor inhibitory efficacy of anti-human PD1 antibodies and anti-human OX40 antibodies was tested in BALB/c-hPD1/hOX40 mice subcutaneously transplanted with CT26 tumor cell line.
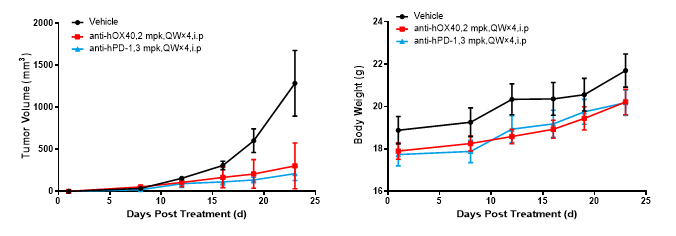
Figure: Mouse tumor growth curve. Bottom Figure: Mouse body weight curve.
(Data from verification studies by third-party partners)
Colon cancer cells CT26.WT in the logarithmic growth phase were subcutaneously inoculated into 6-8 wo BALB/c-hPD1/hOX40 humanized mice. The mice were randomized into 3 Groups (Control Group, OX40 Antibody Group and PD1 Antibody Group; 6 animals/group) on the day of inoculation, and treated with specific antibodies at corresponding dose levels. The drugs were administered once weekly for a total of four doses. The data are presented as Mean ± SEM.
Results: After tumor inoculation into BALB/c-hPD1/hOX40 mice, the mice were treated with anti-human OX40 and anti-human PD-1 antibodies, respectively, and good antitumor effect was observed in both groups.
This demonstrates that the BALB/c-hPD1/hOX40 mouse is an ideal model for evaluating the in vivo efficacy of anti-human OX40 and anti-human PD-1 antibodies.
References:
[1] OX40 Agonists and Combination Immunotherapy: Putting the Pedal to the Metal. Front Oncol. 2015, 16;5:34.
[2] Control of Immunity by the TNFR-Related Molecule OX40 (CD134). Annu Rev Immunol. 2010, 28:57-78.
[3] OX40 promotes Bcl-xL and Bcl-2 expression and is essential for long-term survival of CD4 T cells. Immunity. 2001, 15(3):445-55.
[4] Robust B cell immunity but impaired T cell proliferation in the absence of CD134 (OX40). J Immunol. 1999,15;163(12):6520-9.
[5] Cross-linking of OX40 ligand, a member of the TNF/NGF cytokine family, induces proliferation and differentiation in murine splenic B cells. Immunity. 1995,2(5):507-21.

