Glucocorticoid-induced TNFR-related protein (GITR), a member of the TNF receptor superfamily, is expressed in several cells, including T-cells. GITR, which is upregulated in activated T-cells, is a costimulatory signal of T-cells [1], and its ligand (GITRL) is mainly expressed in dendritic cells (DCs), macrophages, and B-cells. GITR/GITRL have multiple essential functions and play important roles in the regulation of T-cell proliferation and the treatment of tumors and autoimmune diseases [3, 4]. In clinical cancer treatment studies, drugs targeting the GITR pathway have broad prospects [2]; preclinical studies showed the application of GITR agonists alone or in combination with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors or CTLA-4 inhibitors had promising results in the treatment of some solid tumors.
Development Strategy
GemPharmatech has successfully developed the BALB/c-hPD1/hGITR model by replacing the GITR coding region with humanized GITR in BALB/c-hPD1 mice, confirming it is an ideal animal model for the screening and evaluation of human PD1 inhibitors, anti-GITR antibodies, and combination therapies.
1. BALB/c-hPD1/hGITR: hPD1/hGITR Antibody Drug Efficacy Test
The tumor inhibitory efficacy of anti-human PD1 antibodies and GITR antibodies was tested in BALB/c-hPD1/hGITR mice subcutaneously inoculated with CT26 tumor cell line.
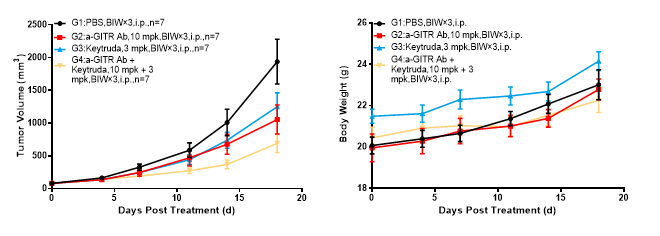
Anti-GITR antibody: BMS986156 analogue
Left Figure: Mouse tumor growth curve Right Figure: Mouse body weight curve
In vivo efficacy test in a model of BALBc-hPD1/hGITR mice subcutaneously inoculated with CT26.WT, murine colon cancer cells CT26.WT in the logarithmic growth phase were transplanted into BALB/c-hPD1/hGITR mice. When tumors reached an average volume of about 100 mm3, the mice were randomized to PBS Group, anti-GITR Ab Monotherapy Group, Keytruda Monotherapy Group, and Anti-GITR Ab + Keytruda Combination Therapy Group (n = 7). They were administered the complementary therapies twice weekly for six doses. The data are presented as Mean ± SEM.
Results: The tumor growth inhibition (TGI) was 46.60% and 38.33%, respectively, in anti-GITR Ab Treatment Group and the Keytruda Treatment Group, suggesting tumor growth inhibitory effect to a certain degree; the TGI was 62.28% in the Anti-GITR Ab + Keytruda Combination Therapy Group, suggesting significant tumor growth inhibitory effect.
This demonstrates that the BALBc-hPD1/hGITR mouse is an ideal animal model for the screening and evaluating of anti-hPD1, GITR antibodies, and combination therapies.
References:
[1].Knee, Deborah A., Becker Hewes, and Jennifer L. Brogdon. “Rationale for anti-GITR cancer immunotherapy.” European journal of cancer 67 (2016): 1-10.
[2].Placke, Theresa, Hans-Georg Kopp, and Helmut Rainer Salih. “Glucocorticoid-induced TNFR-related (GITR) protein and its ligand in antitumor immunity: functional role and therapeutic modulation.” Clinical and Developmental Immunology 2010 (2010).
[3].Clouthier, Derek L., and Tania H. Watts. “Cell-specific and context-dependent effects of GITR in cancer, autoimmunity, and infection.” Cytokine & growth factor reviews 25.2 (2014): 91-106.
[4].Tigue, Natalie J., et al. “MEDI1873, a potent, stabilized hexameric agonist of human GITR with regulatory T-cell targeting potential.” Oncoimmunology 6.3 (2017): e1280645.

