Advance Psoriatic Arthritis Drug Discovery with a Validated Preclinical Model for JAKi and Dexamethasone Testing
August is Psoriasis Awareness Month, a time to raise awareness for psoriasis, a chronic immune-mediated skin condition marked by erythematous plaques, scaling, and dysregulated keratinocyte proliferation. However, the burden can extend beyond the skin. Approximately 30% of psoriasis patients develop psoriatic arthritis (PsA), a progressive inflammatory disease affecting the joints.
Despite advancements in targeted therapies, PsA remains a clinical challenge due to its heterogeneous presentation and undefined pathogenesis. To close this translational gap, there is a growing demand for reliable preclinical models that replicate the manifestations of skin and joint symptoms of PsA. At GemPharmatech, we have developed a robust Mannan/CFA-induced PsA mouse model that faithfully mirrors PsA pathology. Designed for translational impact, this model is ideal for evaluating small molecules (e.g., JAK inhibitors) and biologics in humanized strains.
Accelerate your PsA drug development pipeline with our validated mouse models:
Whether you are working on JAK-STAT signaling or combination immunotherapies, our PsA model delivers the predictive power and reproducibility you need to confidently advance from discovery to IND.
Why This Model?
100% disease incidence in 2 weeks
Recapitulates arthritis & skin pathology
Validated Efficacy Data:
◾ JAK Inhibitors:
40% reduction in clinical scores
Significant inhibition of skin thickening
◾ Dexamethasone:
70% suppression of paw edema
90% decrease in skin thickness
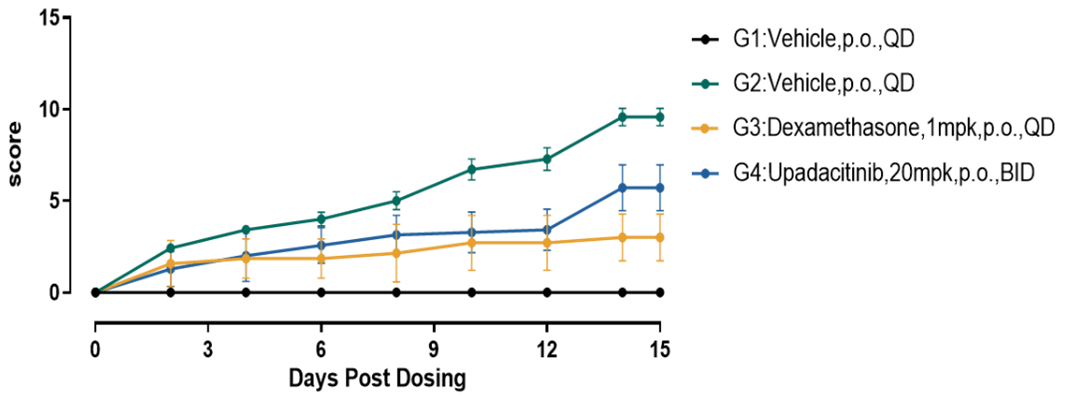
Fig.1 Pharmacodynamic data of DXMA and Upadacitinib in Mannan/CFA induced PsA model
Compared with the model control group, the clinical arthritis score in mice treated with DXMA and Upadacitinib was significantly decreased.
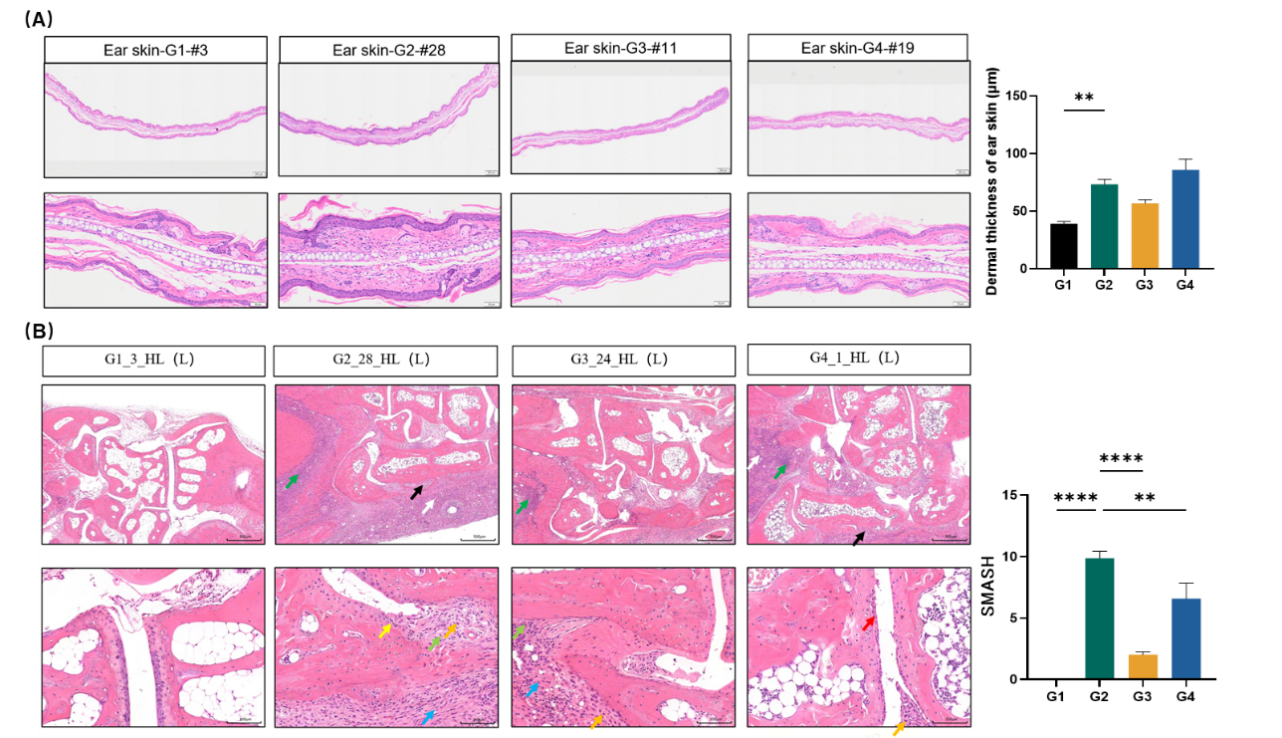
Fig. 2 Histopathological staining results of ears (HE Staining) and joints (HE Staining)
Compared to the healthy control group, the dermal thickness of the ear skin (A), the arthritis pathological score (B) were notably increased in the model group. The dermal thickness of the ear skin in the DXMA-treated group showed a decreasing trend. Following treatments with DXMA and Upadacitinib, the arthritis pathological scores showed significant reductions.
End-to-End Service Support:
◾ Customized dosing regimens
◾ Multi-parameter analysis:
Histopathology (H&E/TRAP)
PASI-like skin scoring
Serum biomarker profiling
Contact our team for cohort availability