Neuroinflammatory pain is a type of chronic pain caused by inflammation in the nervous system. It is typically modeled in animals using pro-inflammatory stimuli such as tissue incision, formalin, or complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA). CFA is a commonly used inflammatory agent that induces strong and sustained immune responses, and it is used to model persistent inflammatory pain in mice.
1. Experimental Design
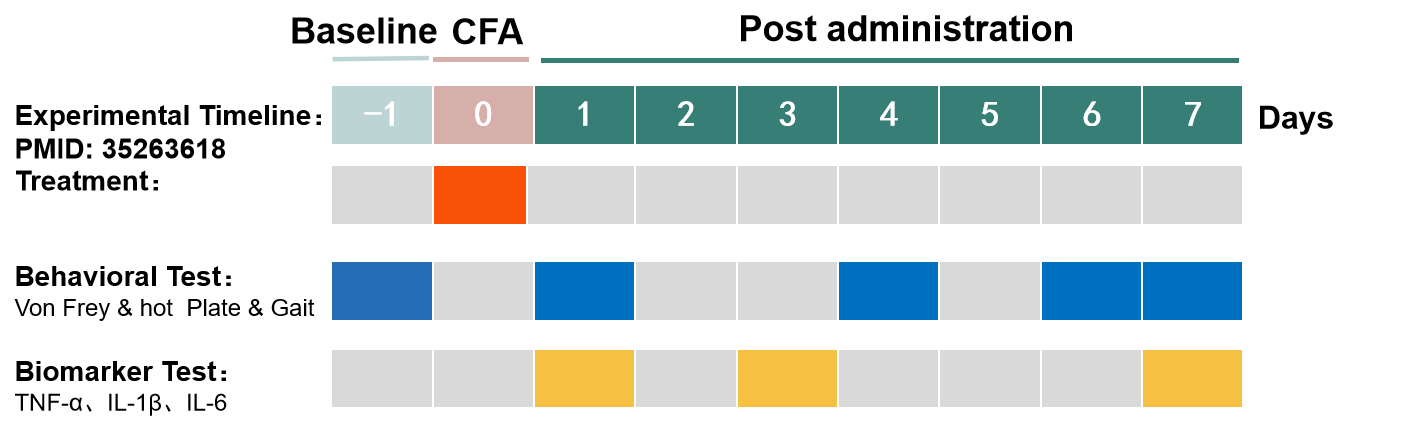
2. Behavioral Test: Von Frey & Hot Plate
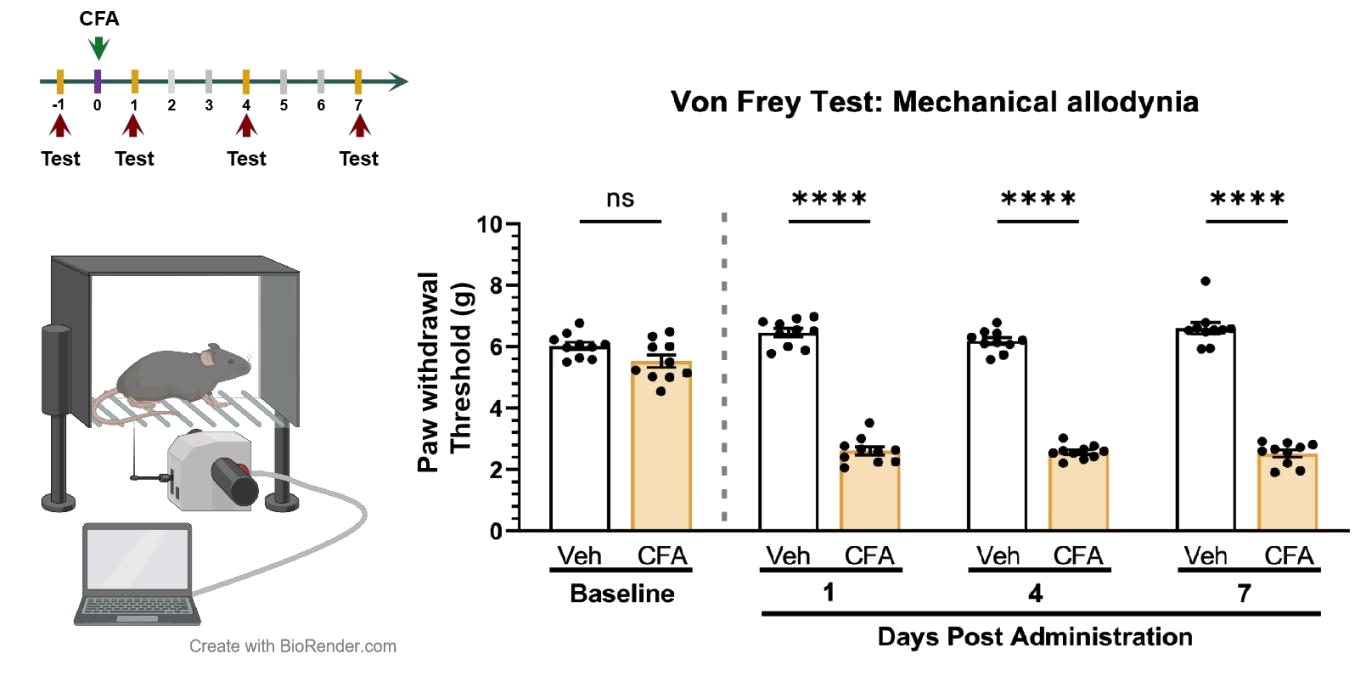
n=10 mice/group, all data represent as MEAN ± SEM, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001, Two-way ANOVA
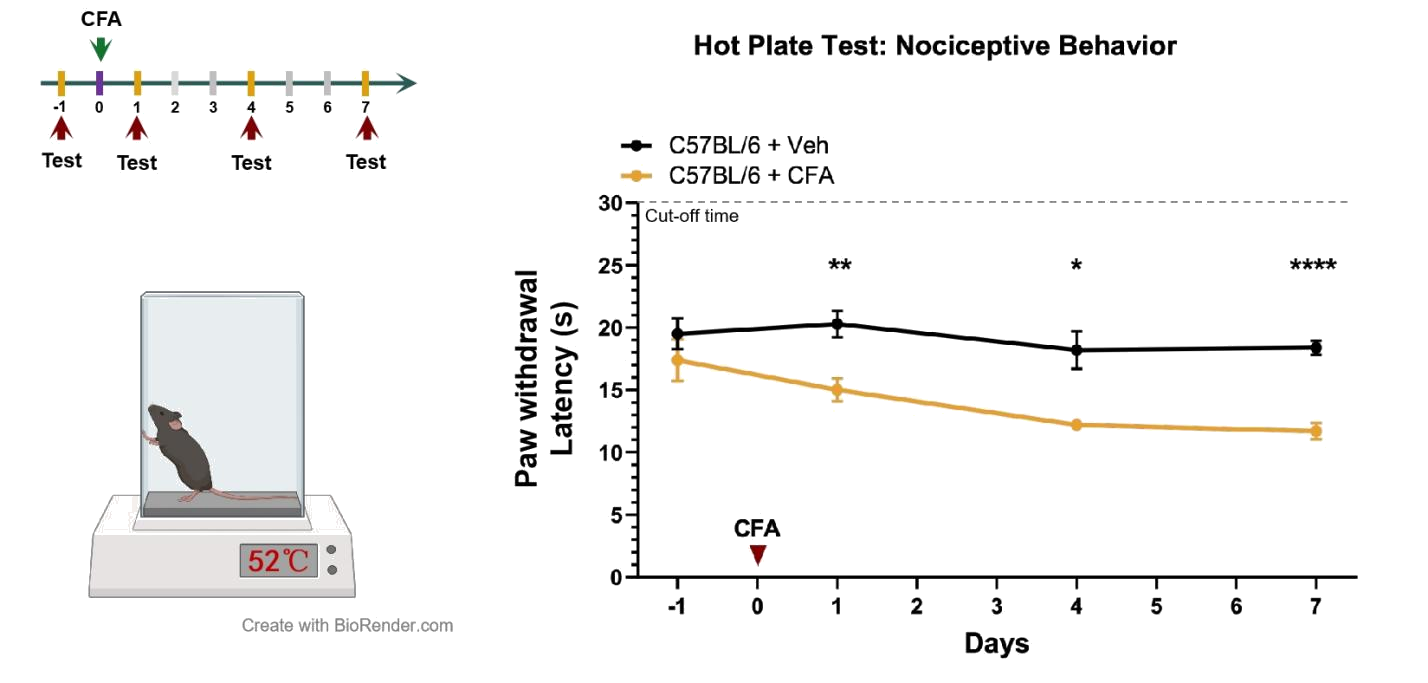
n=10 mice/group, all data represent as MEAN ± SEM, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001, Two-way ANOVA
Mice exhibit a significant decrease in the thresholds for Von Frey mechanical pain and thermal pain stimuli after CFA injection.
3. Molecular: QPCR (Hind paw skin)
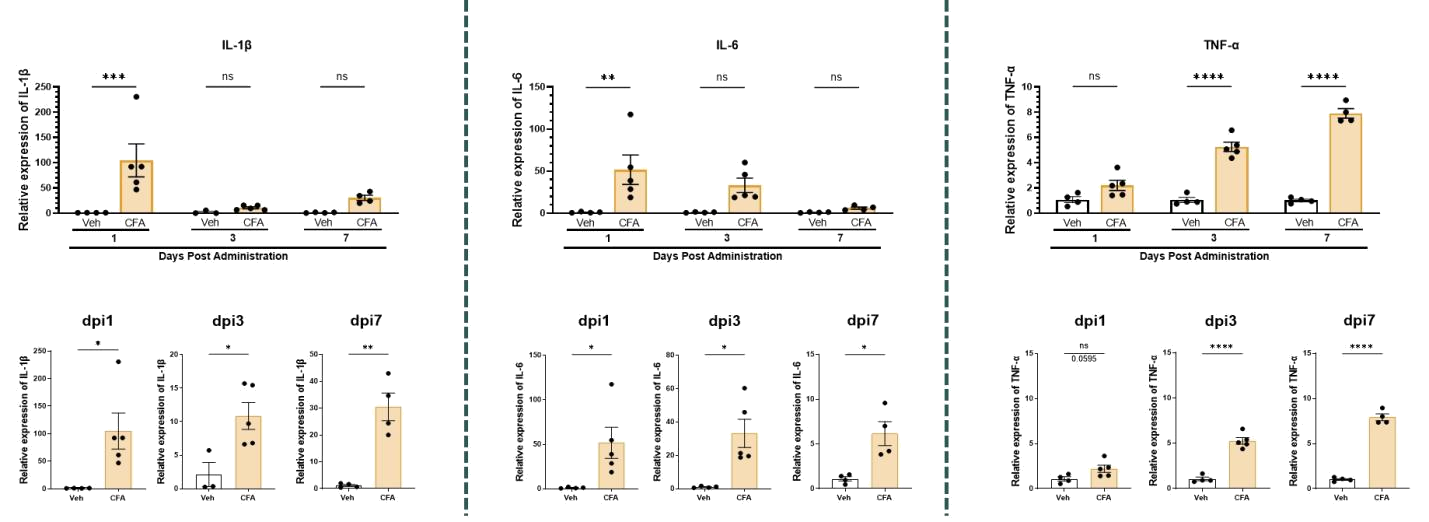
n=4-5 mice/group, all data represent as MEAN ± SEM, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001, Two-way ANOVA, T-test
The expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β in the paw skin of mice is significantly upregulated after CFA injection.