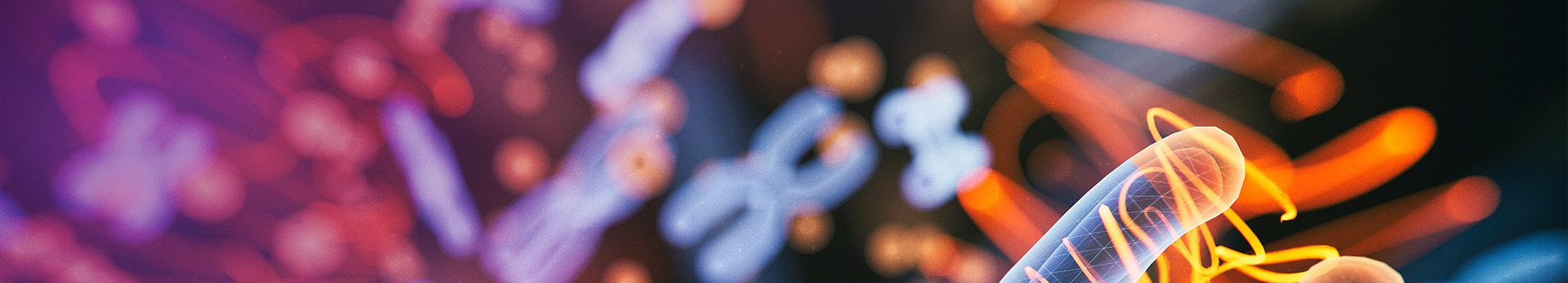Motor function behavioral tests in animal research are a series of experimental paradigms designed to assess the motor capabilities, coordination, balance, strength, and overall motor system integrity in animals. These tests are critical for studying the effects of neurological disorders, genetic modifications, pharmacological treatments, or environmental factors on motor behavior. They are widely used in preclinical research to model human motor dysfunctions, such as those seen in Parkinson's Disease, Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS), Huntington's Disease, and spinal cord injuries.
GemPharmatech provides data using behavioral tests such as the Open Field Test, Rotarod Test, Footprint Test (Catwalk), Grip Strength Test, and Pole Test to detect changes in mouse motor function.
1. Open Field Test
While primarily used to measure general locomotor activity and anxiety-like behavior, this test also provides insights into spontaneous motor activity and exploratory behavior by quantifying the distance traveled, speed, and movement patterns of animals in an open arena.
Open Field Test
2. Rotarod Test
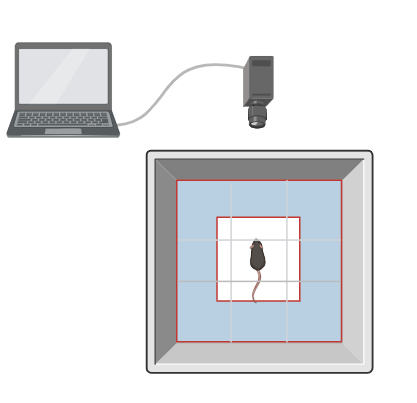
This test assesses motor coordination, balance, and motor learning by placing animals on a rotating rod and measuring the time they can remain on the rod without falling. It is widely used to evaluate the effects of drugs or genetic modifications on motor performance.
Rotarod Test
3. Footprint Test (Catwalk)
This test evaluates locomotor patterns and gait abnormalities by analyzing the footprints or walking patterns of animals. Techniques such as ink-paw printing, video tracking, or automated systems (e.g., CatWalk) are used to measure parameters like stride length, step width, and symmetry.

Footprint (Catwalk) Test
4. Grip Strength Test
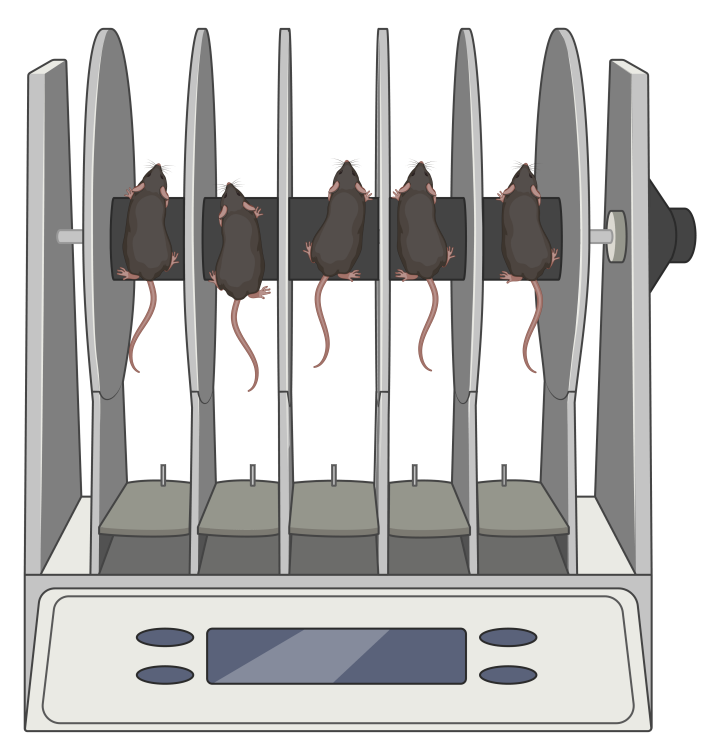
This test measures forelimb and hindlimb muscle strength using a grip strength meter. Animals are allowed to grasp a grid while being gently pulled in the caudal direction, and the force exerted is recorded. It is often used to assess neuromuscular function and the effects of muscle-wasting conditions.
Grip Strength Test
5. Pole Test
This test evaluates motor coordination and bradykinesia (slowness of movement) by timing how long it takes for an animal to descend a vertical pole. It is commonly used in conjunction with Parkinson's disease models.

![]()
Pole Test
All images created in https://BioRender.com.