Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy can be classified based on the type of chemotherapy drug into: taxane-induced, platinum-based, and vinca alkaloid-induced peripheral neuropathies. Platinum-based drugs, such as oxaliplatin, damage dorsal root ganglia, leading to neuronal cell apoptosis and subsequent neurotoxicity.
1. Experimental Design
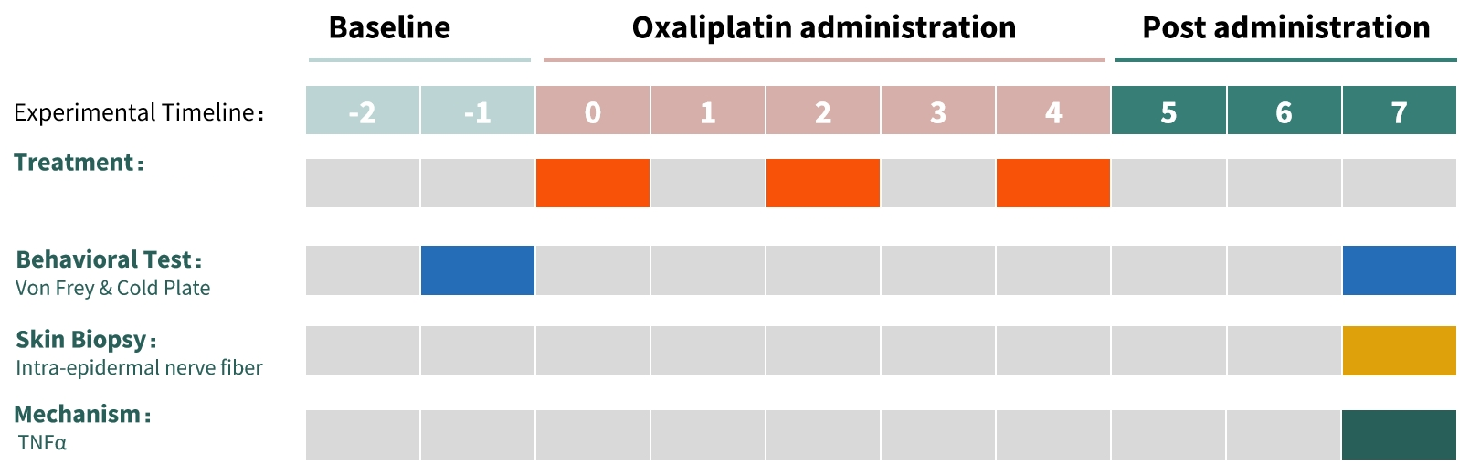
2. Behavioral Test: Von Frey & Cold Plate
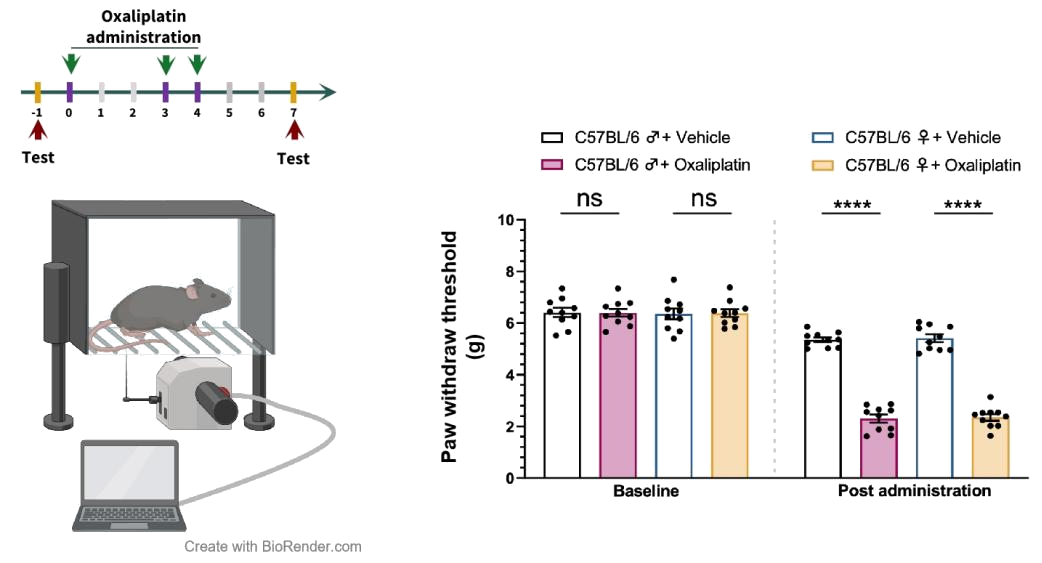
n=10 mice/group, all data represent as MEAN ± SEM, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001, T-Test.
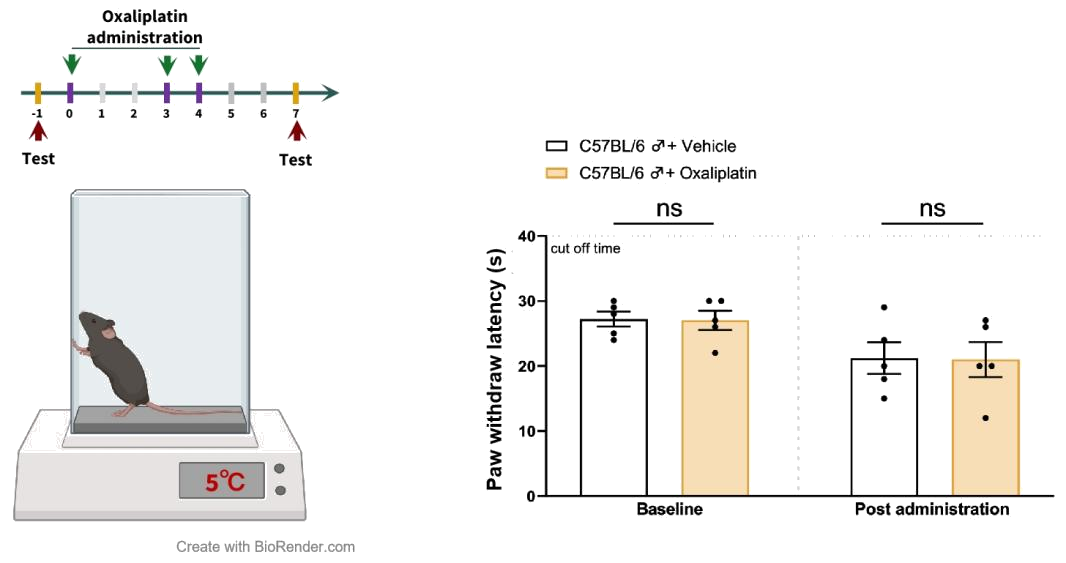
n=5 mice/group, all data represent as MEAN ± SEM, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001, T-Test.
The mechanical pain threshold measured by Von Frey stimuli significantly decreases in mice after oxaliplatin injection.
3. Skin Biopsy: IENF (intraepidermal nerve fiber)
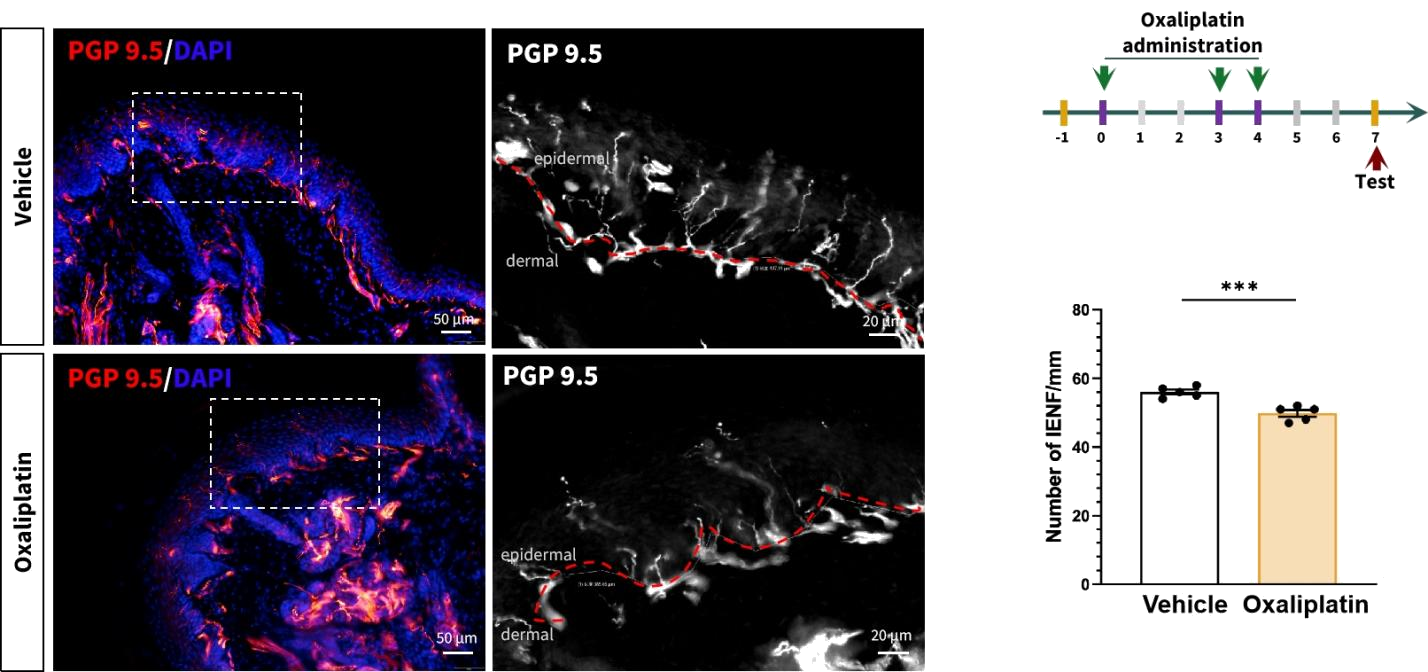
n=5 mice/group, all data represent as MEAN ± SEM, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001, T-Test
The density of intraepidermal nerve fibers (IENF) in the skin decreases in oxaliplatin-induced neuropathic mice.
4. Molecular: TNFα expression in Dorsal Root Ganglion (DRG)
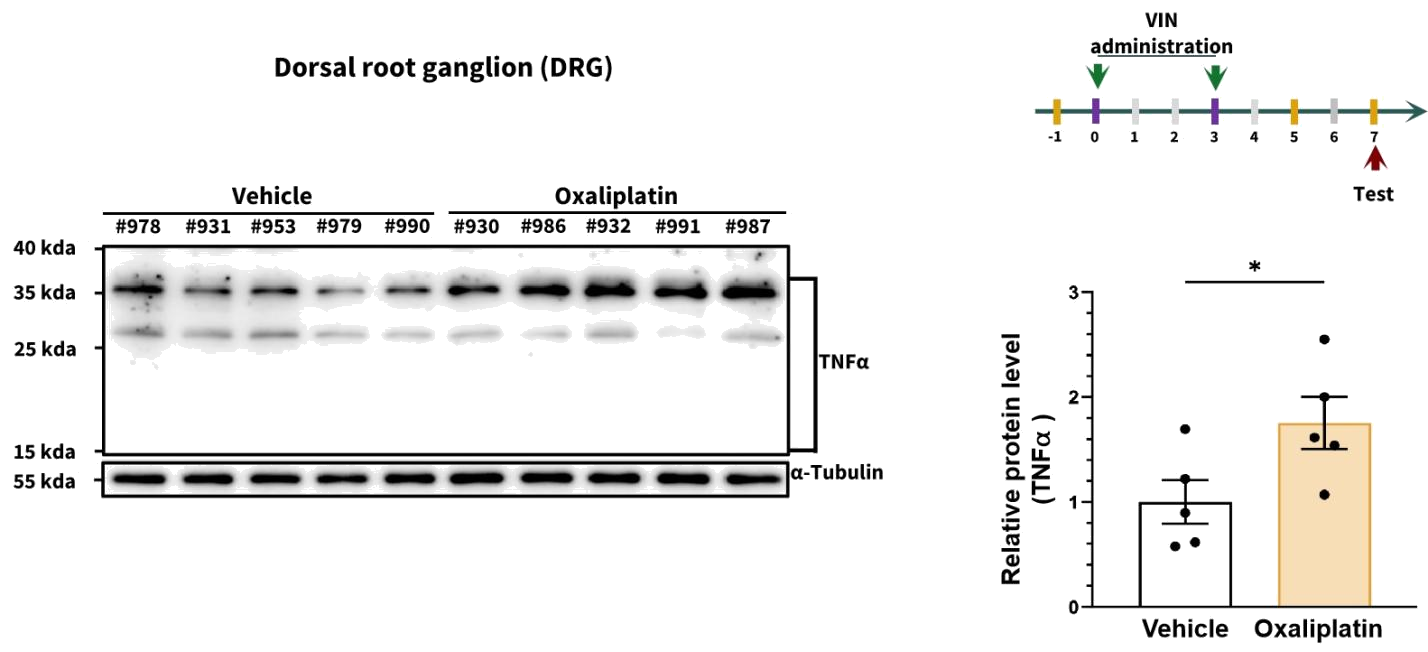
n=5 mice/group, all data represent as MEAN ± SEM, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001, T-Test
The expression of the pro-inflammatory cytokine TNFα in the dorsal root ganglia increases in oxaliplatin-induced neuropathic mice.