Virus infection models in mice are used to study the pathogenesis of viral diseases and evaluate the efficacy of antiviral drugs in a living organism. By infecting mice with specific viruses, we can observe how the virus spreads, replicates, and causes disease symptoms. This allows us to test the ability of experimental drugs to reduce viral load, improve survival rates, and alleviate disease symptoms in a more physiological context.
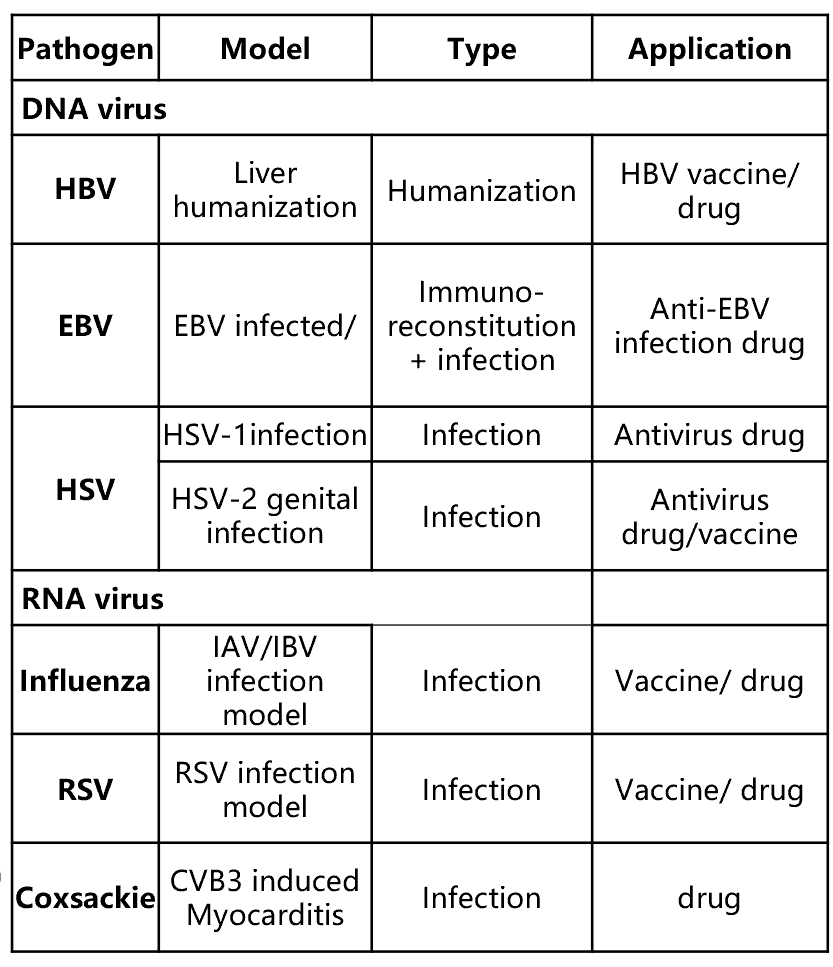
List of viral infection models
Case 1: Influenza vaccine validation in C57BL/6J mice
In this project, we first immunize mice with mRNA vaccines. Subsequently, the immunized mice were infected with H1N1 and the protective effect of the vaccine was observed by monitoring various outcomes, such as the viral load in the mice, the development of disease symptoms, and the survival rate.
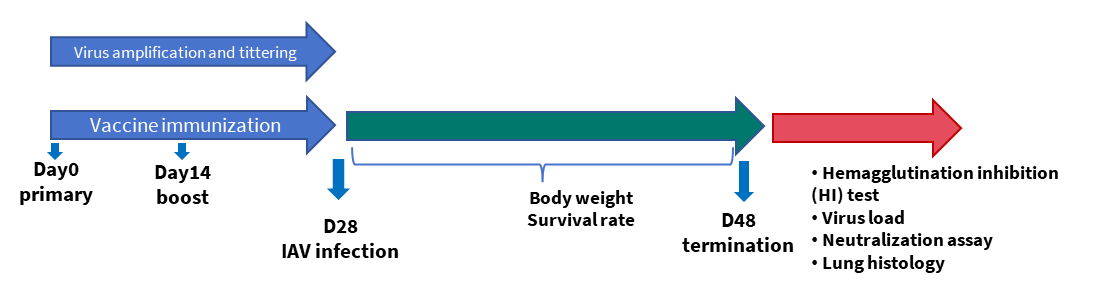
The study outline of influenza vaccine validation
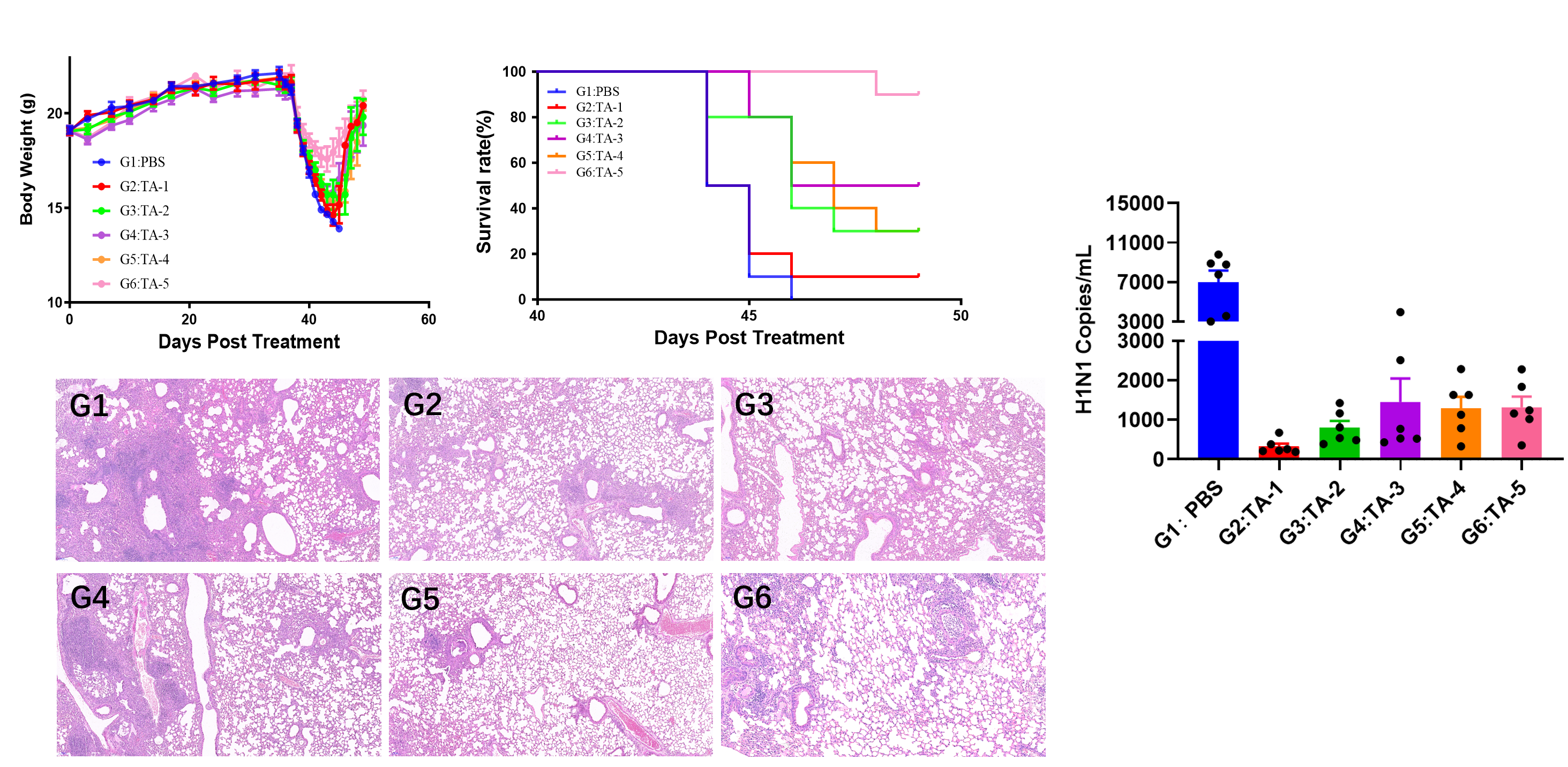
The bodyweight, survival rate, histological changes and viral load examination in H1N1 vaccine validation project
Case 2: Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Animal Model Development
We offer preclinical pharmacodynamic evaluation services for the assessment of small molecules, macromolecules, or vaccines. We possess two important models: the AAV-HBV transduction model and the HBV-infected liver-humanized mouse model.
The AAV-HBV transduction model allows for the efficient delivery of the different genotypes of HBV genome into target cells, mimicking the natural infection process to a certain extent. This model can be used to study the replication and pathogenesis of HBV, as well as to evaluate the efficacy of potential drugs or vaccines.
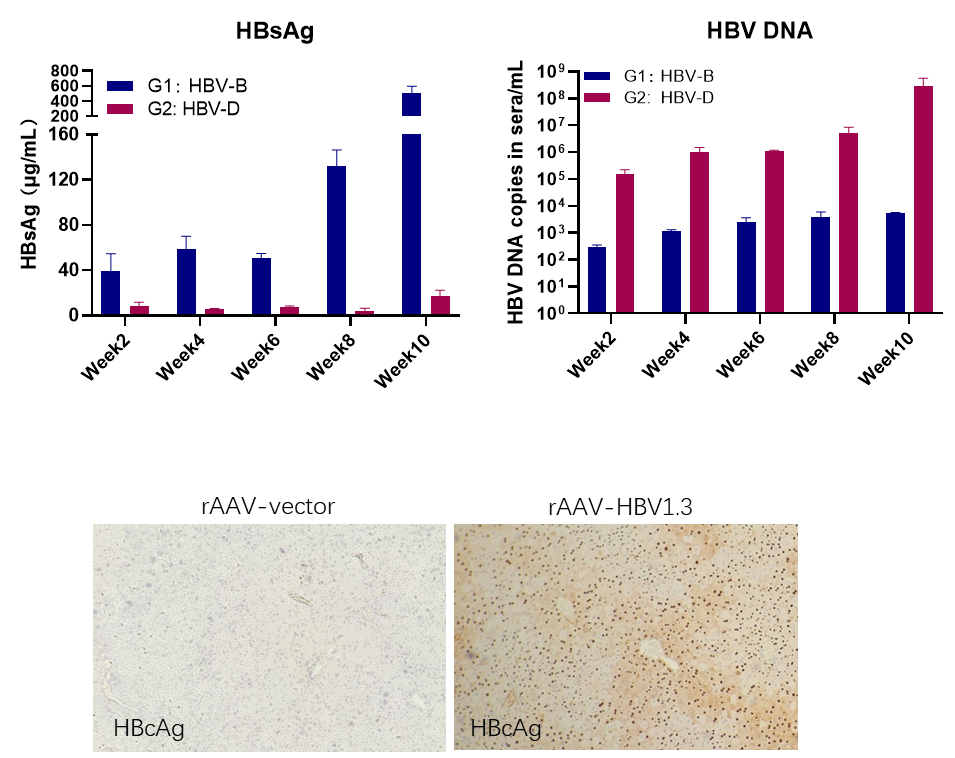
Serum HBsAg, HBV DNA in AAV-HBV-transduced C57BL/6J mouse
The liver-humanized mouse model infected with HBV is a more advanced model that provides a more physiological environment for studying HBV infection.
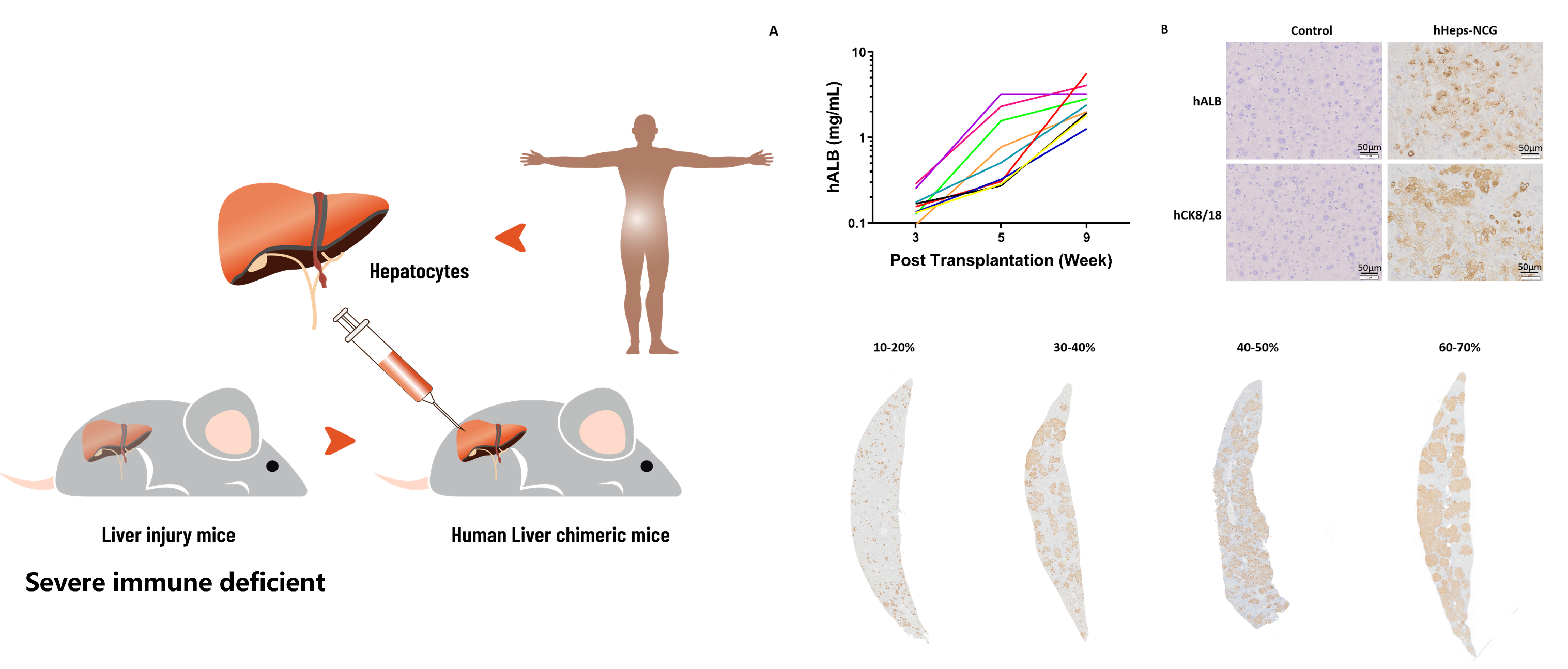
The construction of liver-humanized model in NCG-Fah KO mouse
By reconstituting the human liver microenvironment in mice and then infecting them with HBV, we can closely observe the replication of HBV in mice.
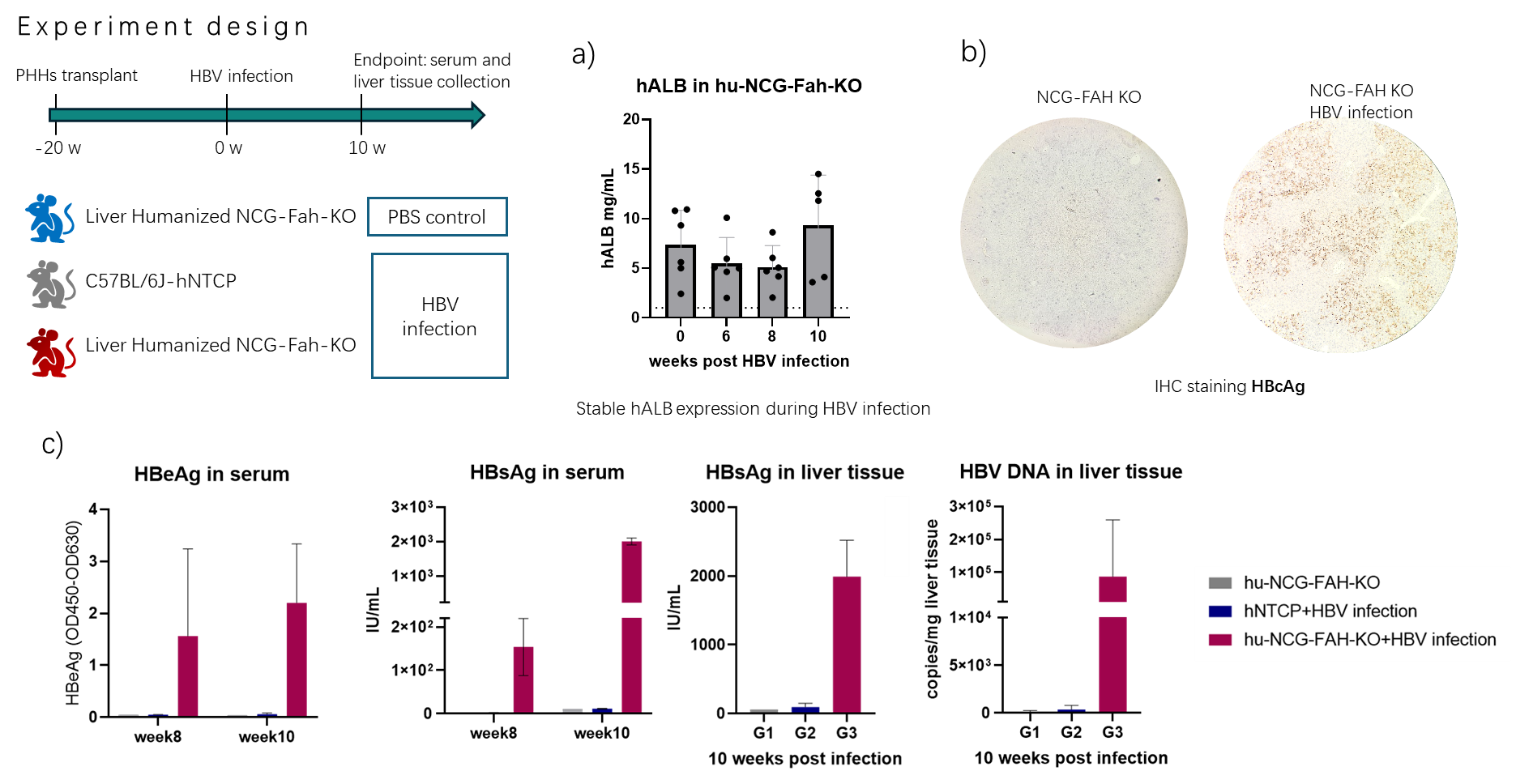
HBV infection in liver-humanized model
These two models enable us to comprehensively evaluate the effectiveness of various compounds and vaccines against HBV, providing crucial data for the development of new treatments and prevention strategies.