Neuroinflammatory pain is a type of chronic pain caused by inflammation in the nervous system. It is typically modeled in animals using pro-inflammatory stimuli such as tissue incision, formalin, or complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA). Formalin injection induces acute inflammatory pain, which can present in two phases: the first phase is characterized by pain behavior due to the direct stimulation of nerve endings immediately after formalin injection, while the second phase occurs approximately 20 minutes after injection and is caused by the persistent nociceptive input resulting from local chronic inflammation.
1. Experimental Design
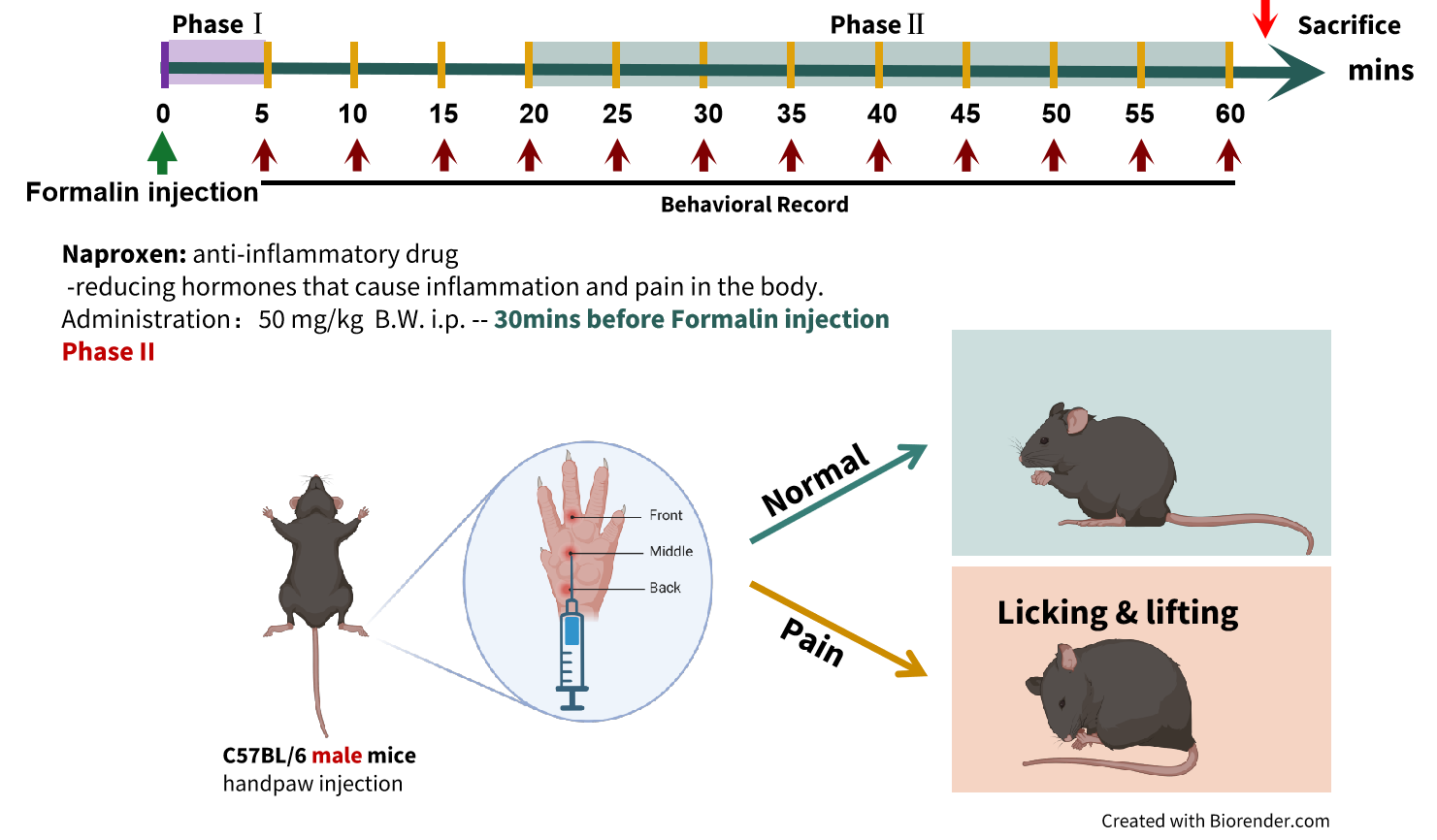
2. Behavioral Test: Licking and lifting
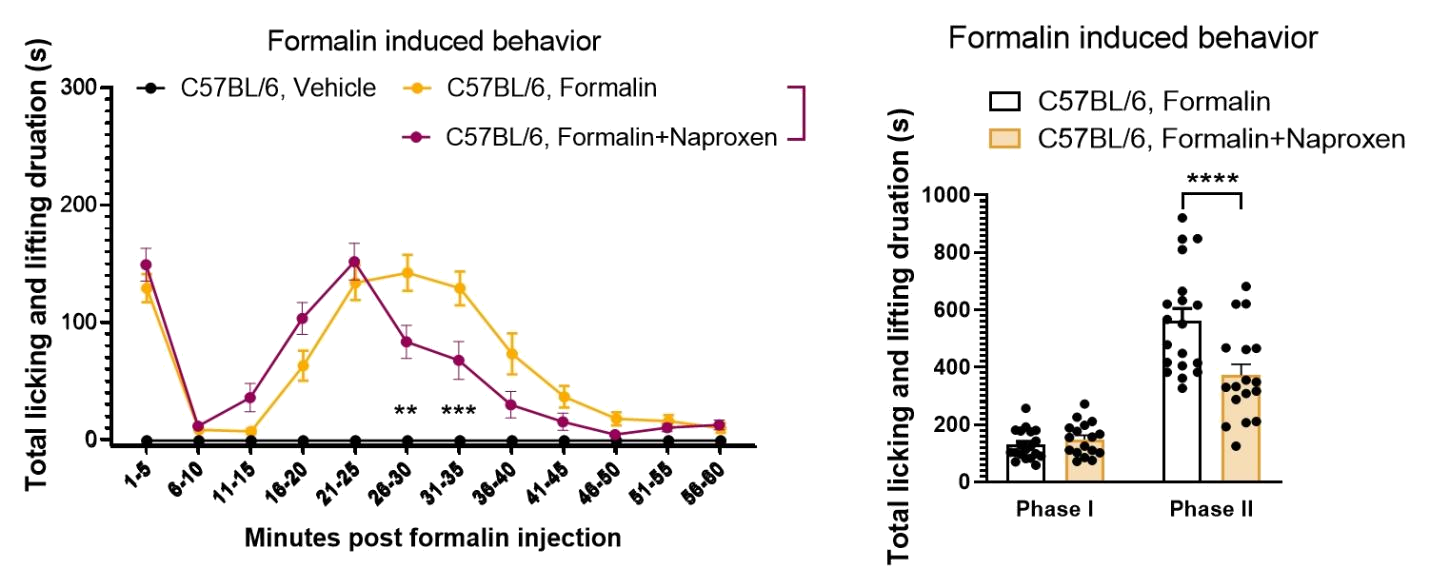
n=10 mice/group, all data represent as MEAN ± SEM, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001, Two-way ANOVA
After formalin injection, mice show increased licking of the injected paw and elevated lifting of the leg. The anti-inflammatory drug Naproxen can reduce the pain response in the second phase of formalin-induced pain mouse model.
3. Molecular: QPCR (Hind paw skin)
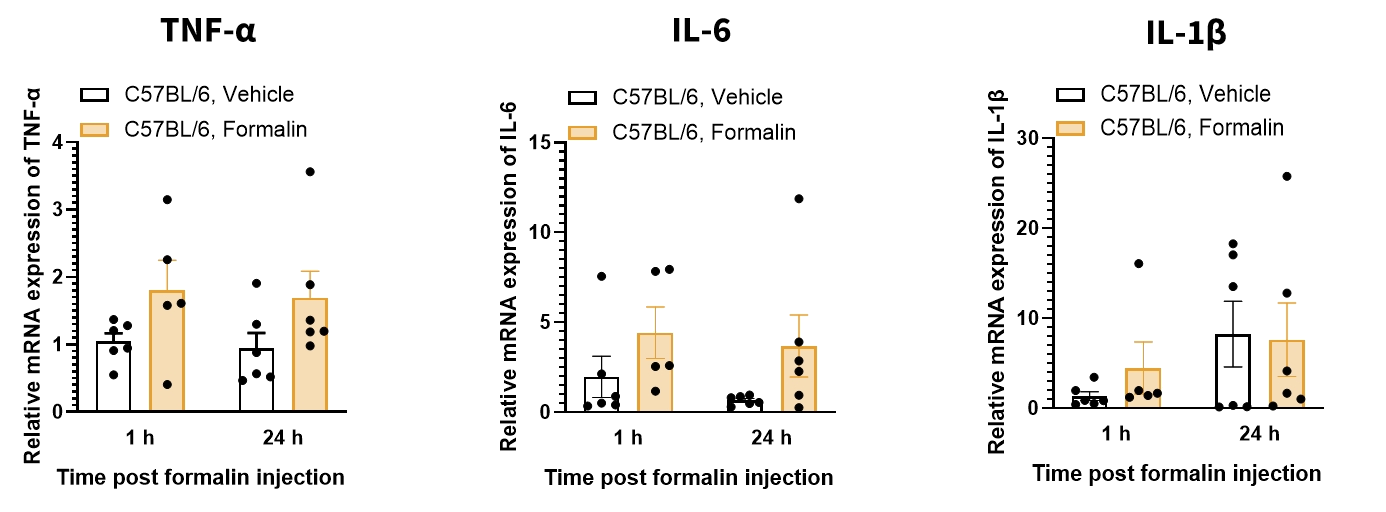
n=2-3 mice/group. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. T-test was performed to determine the statistical significance between 2 groups. *P<0.05,**P<0.01,***P<0.001,****P<0.0001. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
The expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β in the paw skin shows no significant change after formalin injection.