Understanding Rare Diseases: A Global Health Challenge
Rare diseases, often termed "orphan diseases," affect fewer than 1 in 2,000 individuals, yet collectively impact over 350 million people worldwide. There are currently over 7,000 identified rare diseases, 80% of which originate from genetic causes. Many rare diseases such as hemophilia and Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD), often manifest in childhood, leading to severe disabilities or early mortality. Due to limited patient populations and resources, researching the disease pathology and identifying treatment modalities for individual rare diseases have proven difficult. These challenges highlight the need for innovative research approaches and platforms, such as animal models which mimic the origination and phenotype of the diversified diseases.
Why Genetically Engineered Mouse Models (GEMMs) Matter
GEMMs have become indispensable in rare disease research, bridging the gap between molecular insights and therapeutic development. Along with their genetic similarity to humans their main advantages include:
Ease of precision genetic editing: Advanced genome editing technologies allow precise knockouts, knock-ins, or point mutations to mimic human variants.
High Reproducibility: Consistent genotypes and phenotypes ensure study reproducibility.
Ethical and Practical Feasibility: Mice enable large-scale studies impractical in human trials, accelerating drug discovery and evaluation.
GemPharmatech’s Rare Disease Models
As part of GemPharmatech’s commitment to supporting the scientific community with the best preclinical research solutions, we have undertaken an ambitious Knockout All Project (KOAP) to generate knockout and conditional knockout mouse strains for all the coding genes in the mouse genome. As most rare diseases originate from monogenic loss-of-function mutations, GemPharmatech’s library of more than 22,000 knockout and conditional knockout mice is able to cover a broad range of rare disease models. Currently, GemPharmatech has validated over 60 rare disease models, across multiple organs and biological processes. We also provide a one-stop solution for the preclinical evaluation of drug candidates targeting genetic and rare diseases.
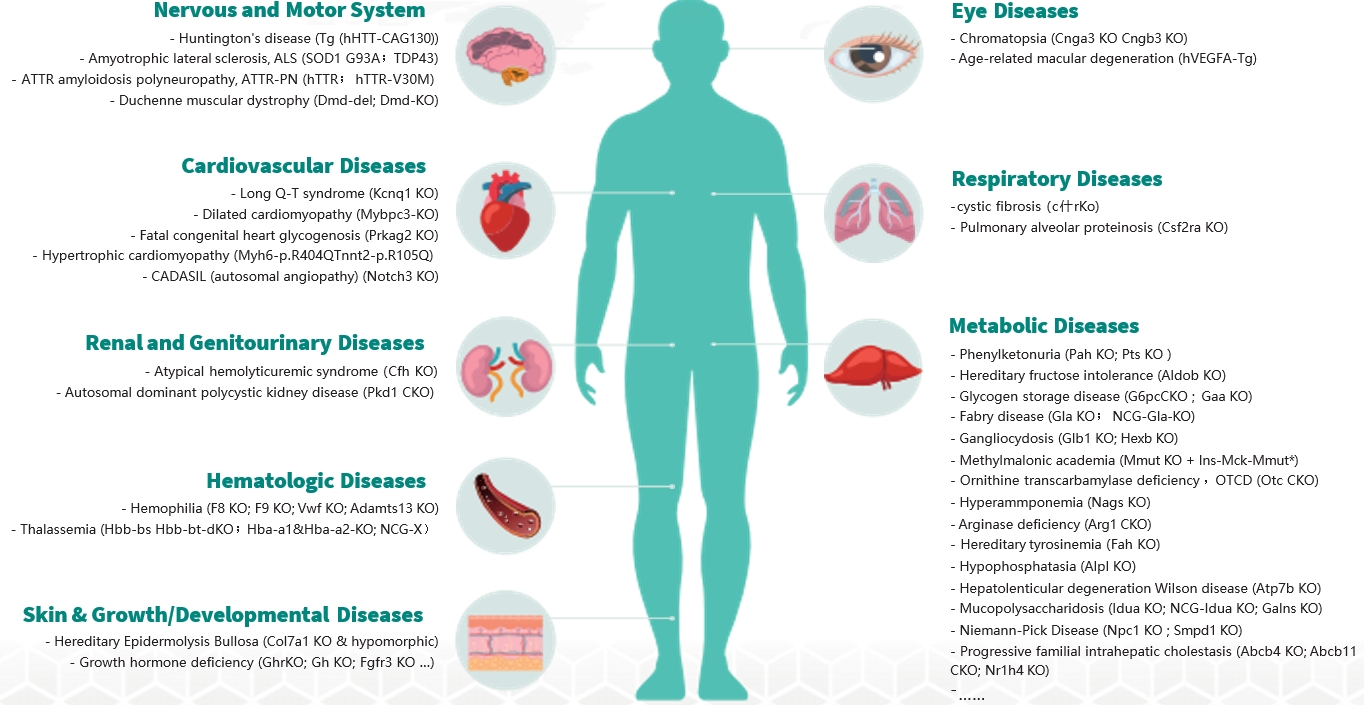
Fig.1 Rare genetic disease resources in GemPharmatech
Conclusion
The success of rare disease research hinges on the availability of robust preclinical models. Mouse models, bolstered by cutting-edge gene-editing tools will continue to play a pivotal role in illuminating disease mechanisms and therapeutic avenues, transforming rare disease care from hope to reality.
Popular Rare Disease Models
Strain Number | Strain Name | Application | Strain Number | Strain Name | Application |
Phenylketonuria | Hemophilia A | ||||
Tyrosinemia | Hemophilia B | ||||
Fabry disease | Fructose intolerance | ||||
Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis | Alpha thalassemia | ||||
Niemann-pick disease type A | Beta thalassemia | ||||
Gangliocydosis type A | Hypoalkaline phosphatasemia |